Replaces Prod. #: BML-GR303
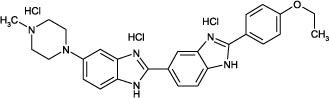
Hoechst 33342 is fluorescent probe useful for detecting DNA by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. Hoechst 33342 may be used on live or fixed cells and is also applicable for cell cycle analysis and monitoring DNA condensation by flow cytometry. An additional ethyl group renders Hoechst 33342 more lipophilic, and thus more readily cell permeable than Hoechst 33258 . Exclusion of Hoechst 33342 dye is a characteristic common to stem cells, as well as chemotherapy-resistant cancer cells. Wavelength Maxima: Excitation 350nm, Emission 461nm
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | 2’-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-5-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2,5’-bi-1H-benzimidazole |
| |
| Formula: | C27H28N6O . 3HCl |
| |
| MW: | 561.9 |
| |
| CAS: | 23491-52-3 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | Yellow solid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in water (50mg/ml) or DMSO (10mg/ml). |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least one year after receipt when stored as recommended. |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light. Keep cool and dry. |
| |
| Technical Info/Product Notes: | This product is a member of the CELLESTIAL® product line, reagents and assay kits comprising fluorescent molecular probes that have been extensively benchmarked for live cell analysis applications. CELLESTIAL® reagents and kits are optimal for use in demanding imaging applications, such as confocal microscopy, flow cytometry and HCS, where consistency and reproducibility are required.
Application Note:
Monitor Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Cancer Cell Lines with a Dual-emission Fluorescent Dye |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
In vivo optical imaging of tumor stromal cells with hypoxia-inducible factor activity: H. Miyabara, et al.; Cancer Sci. (2023),
Abstract;
Parkin regulates neuronal lipid homeostasis through SREBP2-lipoprotein lipase pathway - implications for Parkinson’s disease: W. Tang, et al.; Hum. Mol. Genet.
32, 1466 (2023),
Abstract;
Toward Smart Biomimetic Apatite-Based Bone Scaffolds with Spatially Controlled Ion Substitutions: E. Cianflone, et al.; Nanomaterials
13, 519 (2023),
Abstract;
Alcohol Metabolism Enriches Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cancer Stem Cells That Survive Oxidative Stress via Autophagy: M. Shimonosono, et al.; Biomolecules
11, 1479 (2022),
Abstract;
Enhanced antibacterial activity of Rosehip extract-functionalized Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles: An in vitro and in vivo study: M.M. Alves, et al.; Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces
217, 112643 (2022),
Abstract;
Infection of Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera) Larvae With the Entomopathogenic Fungus Conidiobolus coronatus (Entomophthorales) Induces Apoptosis of Hemocytes and Affects the Concentration of Eicosanoids in the Hemolymph: A.K. Wronska, et al.; Front. Physiol.
12, 774086 (2022),
Application(s): Fluorescence Microscopy and Flow Cytometry of Insect Larval hemocytes,
Abstract;
Intracellular cytokine detection based on flow cytometry in hemocytes from Galleria mellonella larvae: A new protocol: A.K. Wrońska, et al.; PLoS One
17, e0274120 (2022),
Abstract;
Pancreatic tumor microenvironmental acidosis and hypoxia transform gold nanorods into cell-penetrant particles for potent radiosensitization: P.R. Rauta, et al.; Sci. Adv.
8, eabm9729 (2022),
Abstract;
ROS-mediated activation of p38 protects hepatocellular carcinoma cells from caspase-independent death elicited by lysosomal damage: S. Castelli, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol.
198, 114983 (2022),
Abstract;
SARS-CoV2 infection impairs the metabolism and redox function of cellular glutathione: D. Bartolini, et al.; Redox Biol.
45, 102041 (2021),
Abstract;
Full Text
Gadolinium Labelled Nanoliposomes as the Platform for MRI Theranostics: In Vitro Safety Study in Liver Cells and Macrophages: P. Simeckova, et al.; Sci. Rep.
10, 4780 (2020),
Abstract;
Full Text
Cardiac‐specific Mst1 deficiency inhibits ROS‐mediated JNK signalling to alleviate Ang II‐induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis: Z. Cheng, et al.; J. Cell. Mol. Med.
23, 543 (2019),
Application(s): Microplate assay using mouse cardiomyocytes,
Abstract;
Full Text
CD15 Expression Does Not Identify a Phenotypically or Genetically Distinct Glioblastoma Population: E. Kenney-Herbert, et al.; Stem Cells Transl. Med.
4, 822 (2018),
Abstract;
Full Text
Prenatal influenza vaccination rescues impairments of social behavior and lamination in a mouse model of autism: Y. Wu, et al.; J. Neuroinflammation
15, 228 (2018),
Abstract;
Full Text
FOXO3 is essential for CD44 expression in pancreatic cancer cells: M. Kumazoe, et al.; Oncogene
36, 2643 (2017),
Abstract;
Development of alphaviral vectors for macrophage activation in cancer immunotherapy: B. Kurena; (2016), (master's thesis),
Application(s): Cell immunostaining,
Full Text
Carcinogenic activity of PbS quantum dots screened using exosomal biomarkers secreted from HEK293 cells: J.H. Kim, et al.; Int. J. Nanomedicine
10, 5513 (2015),
Application(s): Cell culture of human cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Effects of mechanical stretching on the morphology and cytoskeleton of vaginal fibroblasts from women with pelvic organ prolapse: S. Wang, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci.
16, 9406 (2015),
Application(s): Cell Culture, Microscopy,
Abstract;
Full Text
Utilization of fluorescent probes for the quantification and identification of subcellular proteomes and biological processes regulated by lipid peroxidation products: T.D. Cummins, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med.
59, 56 (2013),
Application(s): Cell Culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
Hormone-induced 14-3-3γ adaptor protein regulates steroidogenic acute regulatory protein activity and steroid biosynthesis in MA-10 Leydig cells: Y. Aghazadeh, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
287, 15380 (2012),
Application(s): Nuclear staining of Adult mouse testis sections,
Abstract;
Full Text
Live-cell assay for detection of apoptosis by dual-laser flow cytometry using Hoechst 33342 and 7-amino-actinomycin D: I. Schmid, et al.; Nat. Protoc.
2, 187 (2007),
Abstract;
High-throughput microtiter assay for Hoechst 33342 dye uptake: G.M. Seigel & L.M. Campbell; Cytotechnology
45, 155 (2004),
Abstract;
Related Products