Product Details
| Clone: | Agr-247 |
| |
| Host: | Mouse |
| |
| Isotype: | IgG1 |
| |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant rat agrin (C-terminal fragment). |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P25304 |
| |
| GenBank ID: | M64780 |
| |
| Source: | Purified from mouse ascites. |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Mouse, Rat
|
| |
| Applications: | IHC, WB
|
| |
| Recommended Dilutions/Conditions: | Immunohistochemistry (10µg/ml)
Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.
Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| |
| Purity Detail: | Protein G affinity purified. |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In PBS, pH 7.2, containing 50% glycerol and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Scientific Background: | Agrin is an essential extracellular matrix component which promotes clustering of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) and other proteins during development at the neuromuscular junction. Agrin, MuSK and Rapsyn are all essential components for AChR aggregation through an unknown mechanism. The C-terminal region of agrin is released into the medium, interacts with receptors on the muscle surface, and induces AChR aggregation. The central region contains two O-linked glycosylation sites and a domain homologous to domain III of laminin. The N-terminal region anchors agrin to the extracellular matrix via other basal membrane components. This region also contains a protease inhibitor domain and glycosaminoglycan attachment sites, increasing the predicted MW from 200kDa to ~600kDa. The diagram shown indicates the domain structure and functional regions of agrin, as well as domains required for AChR aggregation and alpha-dystroglycan and heparin binding. Various agrin isoforms are generated by alternative splicing at the X, Y and Z sites, and differ in the presence or absence of small inserts. The isoforms can determine the biological activity of agrin and their expression in specific tissues and stages of development. While no difference in functional activity has been detected between splicing variants at site X, insertion of a 4 aa peptide at site Y modestly increases agrins nAChR clustering activity. Insertion of an 8 aa peptide at splicing site Z increases the clustering activity of soluble rat agrin 10,000 fold. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
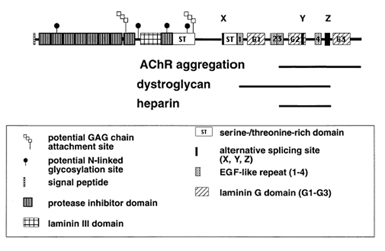
The diagram indicates the domain structure and functional regions of agrin, as well as domains required for AChR aggregation and alpha-dystroglycan and heparin binding.
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Direct Muscle Delivery of GDNF With Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Motor Neuron Survival and Function in a Rat Model of FamilialALS: C. Svendsen, et al. ; Mol. Ther.
16, 2002 (2008),
Application(s): IHC using rat tissue,
Abstract;
Related Products










