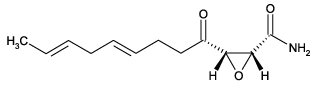
Replaces Prod. #: ALX-380-053
Antibiotic. Fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor reported to bind in equimolar ratio to β-keto-acyl-ACP synthase (KAS; IC50=1.5µM), thus inhibiting protein acylation at concentrations of 45-134 µM. Produces metabolic effects similar to the effects of leptin, but through mechanisms that are independent of, or down-stream from, both leptin and melanocortin receptors. Apoptosis inducer. Inhibitor of bacterial fatty acid synthesis (inhibits FabH, FabB and FabF condensation enzymes).
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | 2,3-Epoxy-4-oxo-7,10-dodecadienamide |
| |
| Formula: | C12H17NO3 |
| |
| MW: | 223.3 |
| |
| CAS: | 17397-89-6 |
| |
| MI: | 14: 2004 |
| |
| RTECS: | JR1670000 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (TLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to off-white solid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DCM (5mg/ml). |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored, as supplied, at -20°C. Stock solutions are stable for up to 3 months at -20°C. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Coordinated Regulation of Membrane Homeostasis and Drug Accumulation by Novel Kinase STK-17 in Response to Antifungal Azole Treatment: C. Hu, et al.; Microbial Spectr.
10, e0012722 (2022),
Abstract;
The Multiple DSF-family QS Signals are Synthesized from Carbohydrate and Branched-chain Amino Acids via the FAS Elongation Cycle: L. Zhou, et al.; Sci. Rep.
5, 13294 (2015),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
Fatty acid synthase inhibitors cerulenin and C75 retard growth and induce caspase-dependent apoptosis in human melanoma A-375 cells: T.S. Ho, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother.
61, 578 (2007),
Abstract;
Expression and functional characterization of a giant Type I fatty acid synthase (CpFAS1) gene from Cryptosporidium parvum: G. Zhu, et al.; Mol. Biochem. Parasitol.
134, 127 (2004),
Abstract;
Identification and molecular characterization of the beta-ketoacyl-[acyl carrier protein] synthase component of the Arabidopsis mitochondrial fatty acid synthase: R. Yasuno, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
279, 8242 (2004),
Abstract;
Key role of mitochondria in cerulenin-mediated apoptosis: S.J. Heiligtag, et al.; Cell Death Differ.
9, 1017 (2002),
Abstract;
Cerulenin mimics effects of leptin on metabolic rate, food intake, and body weight independent of the melanocortin system, but unlike leptin, cerulenin fails to block neuroendocrine effects of fasting: H. Makimura, et al.; Diabetes
50, 733 (2001),
Abstract;
Full Text
Cerulenin-resistant mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with an altered fatty acid synthase gene: J. Inokashi, et al.; Mol. Gen. Genet.
244, 90 (1994),
Abstract;
Effect of cerulenin on the synthesis of very-long-chain fatty acids in microsomes from leek seedlings: F. Schneider, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta
1152, 243 (1993),
Abstract;
Modulation of insulin secretion from normal rat islets by inhibitors of the post-translational modifications of GTP-binding proteins: S.A. Metz, et al.; Biochem. J.
295, 31 (1993),
Abstract;
Studies on cerulenin, 3. Isolation and physico-chemical properties of cerulenin: Y. Sato, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo)
200, 344 (1967),
Abstract;