Product Details
| Alternative Name: | TRP53, Tumor protein p53 |
| |
| MW: | ~70kDa (~85/90kDa observed with GST tag) |
| |
| Source: | Produced in E. coli. Full length human p53 is fused to a GST-tag. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P04637 |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.25 mM DTT, 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM PMSF, 25% glycerol. |
| |
| Purity Detail: | Purified using glutathione sepharose chromatography. |
| |
| Shipping: | Dry Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -80°C |
| |
| Scientific Background: | p53 is a much studied and complex multifunctional protein, which acts as a tumor suppressor in many tumor types and induces growth arrest or apoptosis depending on the physiological circumstances and cell type. It is involved in cell cycle regulation as a trans-activator that acts to negatively regulate cell division by controlling a set of genes required for this process. One of the activated genes is an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. Apoptosis induction appears to be mediated either by stimulation of BAX and FAS antigen expression, or by repression of Bcl-2 expression. The p53 pathway responds to stresses that can disrupt the fidelity of DNA replication and cell division. A stress signal is transmitted to the p53 protein by post-translational modifications. Such modification results in the activation of p53 protein as a transcription factor that initiates a program of cell cycle arrest, cellular senescence or apoptosis. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
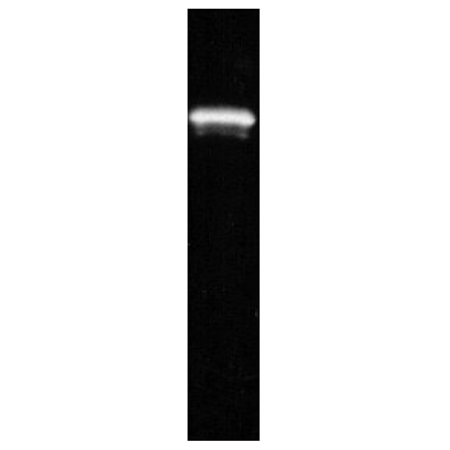
Western blot of prod. no. BML-FW9370 after SDS-PAGE followed by blotting onto PVDF and probing with mouse monoclonal antibody to p53 (Cat. #BML-SA293, 1:5000).
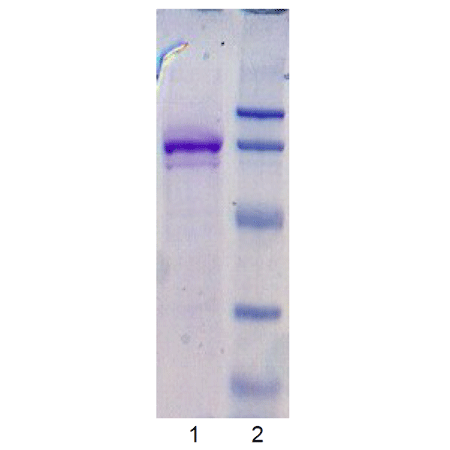
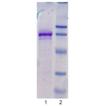
Coomassie stained gel of prod.no. BML-FW9370: Lane 1: FW9370 (3μg), Lane 2: MW markers (top to bottom) 113, 93, 50, 35, and 28 kDa.
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
The ubiquitin ligase LIN41/TRIM71 targets p53 to antagonize cell death and differentiation pathways during stem cell differentiation: D.T.T. Nguyen, et al.; Cell Death Differ.
24, 1063 (2017),
Abstract;
Full Text