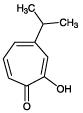
Hinokitiol (β-thujaplicin) is a potent metal chelator that induces differentiation and apoptosis in teratocarcinoma F9 cells and tyrosinase, most likely via metal chelation.
Product Details
| MW: | 164.2 |
| |
| CAS: | 499-44-5 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (GC) |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | Ambient |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and hinokitiol reduce melanin synthesis via decreased MITF production: D. S. Kim, et al.; Arch. Pharm. Res.
27, 334 (2004),
Abstract;
Hinokitiol, a selective inhibitor of the platelet-type isozyme of arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase: H. Suzuki, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.
275, 885 (2000),
Abstract;
Antimicrobial activity and metalloprotease inhibition of hinokitiol-related compounds, the constituents of Thujopsis dolabrata S. and Z. hondai MAK: Y. Inamori, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull.
22, 990 (1999),
Abstract;
Apoptosis during iron chelator-induced differentiation in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells: T. Tanaka, et al.; Cell Biol. Int.
23, 541 (1999),
Abstract;
Induction of apoptosis by hinokitiol, a potent iron chelator, in teratocarcinoma F9 cells is mediated through the activation of caspase-3: Y. Ido, et al.; Cell Prolif.
32, 63 (1999),
Abstract;
Inhibitory effect of beta-thujaplicin on ultraviolet B-induced apoptosis in mouse keratinocytes: T. Baba, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol.
110, 24 (1998),
Abstract;
Full Text