Replaces Prod. #: ALX-350-153
Cell permeable and potent angiogenesis inhibitor from the family of withanolides. Inhibits endothelial cells (HUVEC) sprouting in vitro (IC50=12nM) and in vivo. Exhibits antitumor, anti-inflammatory, radiosensitizing, and immunosuppressive properties. Potently inhibits NF-κB activation by preventing the TNF-induced activation of IκB kinase β (IKKβ). Elicits IKKß hyperphosphorylation concomitant with inhibition of its kinase activity. Affects AP1 transcription and induces cell death. Alters cytoskeletal architecture by covalently binding annexin II and stimulating its basal F-actin cross-linking activity which inhibits the migratory and invasive capability of endothelial cells. Targets the intermediate filament protein vimentin. Displays neuronal regenerative properties. It induced significant regeneration of both axons and dendrites in an A β-induced axonal atrophy model.
Product Details
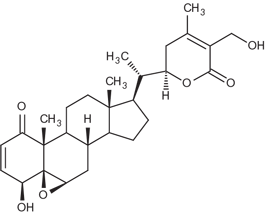
| Alternative Name: | 5,6-Epoxy-4,27-dihydroxy-1-oxowitha-2,24-dienolide |
| |
| Formula: | C28H38O6 |
| |
| MW: | 470.6 |
| |
| Source: | Isolated from Withania somnifera. |
| |
| CAS: | 5119-48-2 |
| |
| MI: | 14: 10048 |
| |
| RTECS: | KE7288500 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | Off-white solid. |
| |
| MeltingPoint: | 241-243°C |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DMSO (20 mg/ml), methanol (10 mg/ml) or 100% ethanol. |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored, as supplied, at -20°C. Stock solutions are stable for up to 3 months at -20°C. |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Withaferin A mitigates metastatic traits in human oral squamous cell carcinoma caused by aberrant claudin-1 expression: J.A. Shin, et al.; Cell Biol. Toxicol.
38, 147 (2021),
Abstract;
Withaferin A induces cell death and differentiation in multiple myeloma cancer stem cells: M.E. Issa & M. Cuendet; Medchemcommun.
8, 112 (2016),
Abstract;
Full Text
Alleviation of Instant Blood-Mediated Inflammatory Reaction in Autologous Conditions through Treatment of Human Islets with NF-κB Inhibitors: M.A. Kanak, et al.; Transplantation
98, 578 (2015),
Application(s): Treatment of culstures Islets,
Abstract;
Full Text
The tumor inhibitor and antiangiogenic agent withaferin A targets the intermediate filament protein vimentin: P. Bargagna-Mohan, et al.; Chem. Biol.
14, 623 (2007),
Abstract;
Withaferin a strongly elicits IkappaB kinase beta hyperphosphorylation concomitant with potent inhibition of its kinase activity: M. Kaileh, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
282, 4253 (2007),
Abstract;
Full Text
Actin microfilament aggregation induced by withaferin A is mediated by annexin II: R.R. Falsey, et al.; Nat. Chem. Biol.
2, 33 (2006),
Abstract;
Neuritic regeneration and synaptic reconstruction induced by withanolide: A: T. Kuboyama, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol.
144, 961 (2005),
Abstract;
Full Text
Withaferin A is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis: R. Mohan, et al.; Angiogenesis
7, 115 (2004),
Abstract;
Growth inhibition of human tumor cell lines by withanolides from Withania somnifera leaves: B. Jayaprakasam, et al.; Life Sci.
74, 125 (2003),
Abstract;
In vivo growth inhibitory and radiosensitizing effects of withaferin A on mouse Ehrlich ascites carcinoma: P.U. Devi, et al.; Cancer Lett.
95, 189 (1995),
Abstract;
Tumor inhibitors. XXXIX. Active principles of Acnistus arborescens. Isolation and structural and spectral studies of withaferin A and withacnistin: S.M. Kupchan, et al.; J. Org. Chem.
34, 3858 (1969),
Abstract;