Replaces Prod. #: ALX-350-016
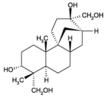
Produced by Cephalosporium aphidicola and other fungi. A diterpene fungal metabolite that acts as reversible inhibitor of eukaryotic nuclear DNA replication. Useful for cell synchronization. Blocks the cell cycle at early S phase. Prolongs the half life of DNA methyltransferase. Specific inhibitor of DNA polymerase α and δ in eukaryotic cells and in some viruses of animal origin. Acts synergistically with vincristine and doxorubicin. Apoptosis inhibitor/inducer.
Product Details
| Formula: | C20H34O4 |
| |
| MW: | 338.5 |
| |
| CAS: | 38966-21-1 |
| |
| MI: | 14: 727 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (TLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to off-white solid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml) or ethanol (25mg/ml). |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored, as supplied, at -20°C. Stock solutions are stable for up to 3 months at -20°C. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Replication stress drives chromosomal instability in fibroblasts of childhood cancer survivors with second primary neoplasms: S. Zahnreich, et al.; DNA Repair (Amst.)
122, 103435 (2023),
Abstract;
Compromised repair of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in Fanconi anemia fibroblasts in G2: S. Zahnreich, et al.; DNA Repair.
96, 102992 (2020),
Abstract;
Aphidicolin and bleomycin induced chromosome damage as biomarker of mutagen sensitivity: a twin study: B. Tedeschi, et al.; Mutat. Res.
546, 55 (2004),
Abstract;
Cytotoxicity of aphidicolin and its derivatives against neuroblastoma cells in vitro: synergism with doxorubicin and vincristine: M. Michaelis, et al.; Anticancer Drugs
11, 479 (2000),
Abstract;
Effect of aphidicolin on DNA methyltransferase in the nucleus: I. Suetake, et al.; Cell Struct. Funct.
23, 137 (1998),
Abstract;
Coordinate regulation of G- and C strand length during new telomere synthesis: X. Fan and C.M. Price; Mol. Biol. Cell
8, 2145 (1997),
Abstract;
Full Text
Dissociation of nuclear and cytoplasmic cell cycle progression by drugs employed in cell synchronization: L. Urbani, et al.; Exp. Cell. Res.
219, 159 (1995),
Abstract;
Drug-induced apoptosis is not necessarily dependent on macromolecular synthesis or proliferation in the p53-negative human prostate cancer cell line PC-3: M.M. Borner, et al.; Cancer Res.
55, 2122 (1995),
Abstract;
TrkA neurogenic receptor regulates differentiation of neuroblastoma cells: W. Poluha, et al.; Oncogene
10, 185 (1995),
Abstract;
Antitumor activity and biochemical effects of aphidicolin glycinate (NSC 303812) alone and in combination with cisplatin in vivo: P.J. O'Dwyer, et al.; Cancer Res.
54, 724 (1994),
Abstract;
Life, death and genomic change in perturbed cell cycles: R.T. Schimke, et al.; Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B Biol. Sci.
345, 311 (1994),
Abstract;
A general protocol for evaluating the specific effects of DNA replication inhibitors: V. Levenson & J.L. Hamlin; Nucleic Acids Res.
21, 3997 (1993),
Abstract;
Aphidicolin potentiates apoptosis induced by arabinosyl nucleosides in human myeloid leukemia cell lines: K. Kuwakado, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol.
46, 1909 (1993),
Abstract;
Aphidicolin: a specific inhibitor of nuclear DNA replication in eukaryotes: S. Spadari, et al.; TIBS 7, 29 (1982),
New views of the biochemistry of eucaryotic DNA replication revealed by aphidicolin, an unusual inhibitor of DNA polymerase alpha: J.A. Huberman; Cell
23, 647 (1981),
Abstract;
Inhibition by aphidicolin of cell cycle progression and DNA replication in sea urchin embryos: S. Ikegami, et al.; J. Cell. Physiol.
100, 439 (1979),
Abstract;
Aphidicolin prevents mitotic cell division by interfering with the activity of DNA polymerase-alpha: S. Ikegami, et al.; Nature
275, 458 (1978),
Abstract;
The production of aphidicolin by Nigrospora sphaerica: A.N. Starratt & S.R Loschiavo; Can. J. Microbiol.
20, 416 (1974),
Abstract;
X-Ray crystallographic determination of the structure of the antibiotic aphidicolin: a tetracyclic diterpenoid containing a new ring system: K.M. Brundret, et al.; J. C. S. Chem. Commun. 1027 (1972),