Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Apoptosis protease-activating factor 1 |
| |
| Clone: | 2E12 |
| |
| Host: | Rat |
| |
| Isotype: | IgG2a |
| |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant human Apaf-1 (apoptosis protease-activating factor 1) N-terminal CARD and CED-4 homologous domains (aa 1-464) . |
| |
| UniProt ID: | O14727 |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human
|
| |
| Specificity: | Recognizes the CARD domain of Apaf-1. |
| |
| Crossreactivity: | Does not cross-react with mouse or rat Apaf-1. |
| |
| Applications: | ELISA, ICC, IHC (FS), IP, WB
|
| |
| Recommended Dilutions/Conditions: | Immunohistochemistry (EM on frozen sections; for details see G. Hausmann, et al., below.)
Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.
Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| |
| Purity Detail: | Protein G-affinity purified. |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide. |
| |
| Handling: | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Short Term Storage: | +4°C |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
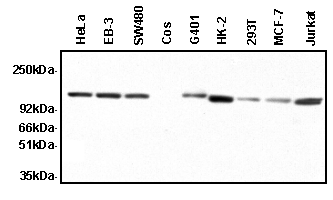
Figure: Western blot analysis with anti-Apaf-1 (human) MAb (clone 2E12) revealing endogenous Apaf-1. Lysates from 106 HeLa, MCF-7, 293T, COS, Jurkat, and activated primary human T cells were probed with clone 2E12. COS (monkey) cells were used as a negative control.

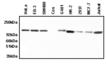
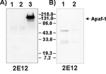
Figures: Species cross-reactivity of MAb to Apaf-1 (clone 2E12) (
ALX-804-348) by Western blot.
A: Lysates from 1-day-old
mouse brain (lane 1), adult
mouse brain (lane 2) and SH-SY5Y
human neuroblastoma cell line (lane 3) were probed with clone 2E12.
B: Lysates from 2-days-old
rat brain (lane 1) and adult
rat brain (lane 2) were probed with clone 2E12.
Results: 2E12 is human specific and does not cross-react with mouse or rat Apaf-1."
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
BOK and NOXA Are Essential Mediators of p53-dependent Apoptosis: A.G. Yakovlev, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
279, 28367 (2004),
Abstract;
Induced inhibition of ischemic/hypoxic injury by APIP, a novel Apaf-1-interacting protein: D.H. Cho, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
279, 39942 (2004),
Abstract;
Full Text
Anti-Fas antibody-induced apoptosis and its signal transduction in human gastric carcinoma cell lines: K. Adachi, et al.; Int. J. Oncol.
23, 713 (2003),
Abstract;
Pro-apoptotic apoptosis protease-activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) has a cytoplasmic localization distinct from Bcl-2 or Bcl-x(L): G. Hausmann, et al.; J. Cell Biol.
149, 623 (2000),
Abstract;
Full Text
Bcl-2 family members do not inhibit apoptosis by binding the caspase activator Apaf-1: K. Moriishi, et al.; PNAS
96, 9683 (1999),
Abstract;
Full Text
General Literature References
Apaf1 in developmental apoptosis and cancer: how many ways to die?: F. Cecconi & P. Gruss; Cell. Mol. Life Sci.
58, 1688 (2001), (Review),
Abstract;
Apaf1 (CED-4 homolog) regulates programmed cell death in mammalian development: F. Cecconi, et al.; Cell
94, 727 (1998),
Abstract;
Bcl-XL interacts with Apaf-1 and inhibits Apaf-1-dependent caspase-9 activation: Y. Hu, et al.; PNAS
95, 4386 (1998),
Abstract;
Full Text
Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3: H. Zou, et al.; Cell
90, 405 (1997),
Abstract;
Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade: P. Li, et al.; Cell
91, 479 (1997),
Abstract;