U.S. Export License required for shipment outside the U.S.
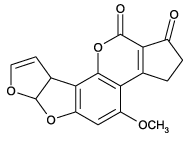
Naturally occuring mycotoxin produced by many species of Aspergillus. Metabolized by the liver to the reactive intermediate aflatoxin M1. Exposure may produce acute necrosis, cirrhosis and carcinoma of the liver. Induces DNA damage.
Product Details
| Formula: | C17H12O6 |
| |
| MW: | 312.3 |
| |
| Source: | Isolated from Aspergillus flavus. |
| |
| CAS: | 1162-65-8 |
| |
| MI: | 14: 180 |
| |
| RTECS: | GY1925000 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC, TLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to yellow powder. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) or methylene chloride (10mg/ml). |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | May be stored in solution for at least three to four weeks at -20°C. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Taxonomic Characterization, Evaluation of Toxigenicity, and Saccharification Capability of Aspergillus Section Flavi Isolates from Korean Traditional Wheat-Based Fermentation Starter Nuruk: J. Bal, et al.; Mycobiology
44, 155 (2016),
Application(s): Positive control, TLC,
Abstract;
Full Text
Antimutagenic Effect of the Ellagic Acid and Curcumin Combinations: H. Zoubkova, et al.; J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol.
5, 296 (2015),
Application(s): In vivo, bone marrow micronucleus test in mice ,
Full Text
Mycotoxin occurrence on baled and pit silages collected in Co. Meath: C. McElinney, et al.; Irish J. Agr. Food. Res.
54, 87 (2015),
Application(s): Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for Mycotoxin analysis,
Full Text
Aflatoxin B1-induced DNA damage and its repair: L. L. Bedard & T. E. Massey; Cancer Lett.
241, 174 (2006), (Review),
Abstract;
Hyperplasia, partial hepatectomy, and the carcinogenicity of aflatoxin B1: B.D. Roebu; J. Cell. Biochem.
91, 242 (2004), (Review),
Abstract;
Activation and detoxication of aflatoxin B1: F.P. Guengerich, et al.; Mutat. Res.
402, 121 (1998), (Review),
Abstract;
Aflatoxin B1 induced lacI mutation in liver and kidney of transgenic mice C57BL/6N: effect of phorone: H. Autrup, et al.; Mutagenesis
11, 69 (1996),
Abstract;
A follow-up study of urinary markers of aflatoxin exposure and liver cancer risk in Shanghai, People's Republic of China: G.S. Qian, et al.; Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev.
3, 3 (1994),
Abstract;
Molecular dosimetry of aflatoxin exposure: contribution to understanding the multifactorial etiopathogenesis of primary hepatocellular carcinoma with particular reference to hepatitis B virus: C.P. Wild, et al.; Environ. Health Perspect.
99, 115 (1993),
Abstract;