Replaces Prod. #: BML-GR338
A potent and specific nuclear export inhibitor. Leptomycin B alkylates and inhibits CRM1/exportin 1, a protein required for nuclear export of proteins containing a nuclear export sequence (NES). In addition to antifungal and antibacterial activities, blocks the cell cycle and is a potent anti-tumor agent. At low nM concentrations, blocks the nuclear export of many proteins including HIV-1 Rev, MAPK/ERK, and NF-κB/IκB and it stabilizes the expression of p53. Other proteins that are influenced by leptomycin B are actin, c-Abl, cyclin B1, MDM2/p53, Iκb, MPF and PKA. Leptomycin B also inhibits the export and translation of many RNAs, including COX-2 and c-Fos mRNAs, by inhibiting export of ribonucleoproteins.
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | LMB |
| |
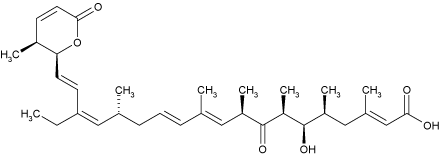
| Formula: | C33H48O6 |
| |
| MW: | 540.7 |
| |
| Source: | Isolated from Streptomyces sp. |
| |
| CAS: | 87081-35-4 |
| |
| Formulation: | Solution in 100% ethanol. |
| |
| Purity: | ≥96% (HPLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | Liquid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in methanol or 100% ethanol; insoluble in water. Unstable in DMSO. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light. Packaged under inert gas. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
AurkA nuclear localization is promoted by TPX2 and counteracted by protein degradation: I.A. Asteriti, et al.; Life Sci. Alliance
6, e202201726 (2023),
Abstract;
Ratjadone and leptomycin B block CRM1-dependent nuclear export by identical mechanisms: T. Meissner, et al.; FEBS Lett.
576, 27 (2004),
Abstract;
Nuclear export of MAP kinase (ERK) involves a MAP kinase kinase (MEK)-dependent active transport mechanism: M. Adachi, et al.; J. Cell. Biol.
148, 849 (2000),
Abstract;
Leptomycin B inactivates CRM1/exportin 1 by covalent modification at a cysteine residue in the central conserved region: N. Kudo, et al.; PNAS
96, 9112 (1999),
Abstract;
CRM1 is responsible for intracellular transport mediated by the nuclear export signal: M. Fukuda, et al.; Nature
390, 308 (1997),
Abstract;
Effects of leptomycin B on the cell cycle of fibroblasts and fission yeast cells: M. Yoshida, et al.; Exp. Cell Res.
187, 150 (1990),
Abstract;
Leptomycins A and B, new antifungal antibiotics. I. Taxonomy of the producing strain and their fermentation, purification and characterization: T. Hamamoto, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo)
36, 639 (1983),
Abstract;