Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Endoplasmin, Tra1, Hsp90B1, Gp96 |
| |
| Host: | Rabbit |
| |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide corresponding to the sequence near the C-terminus of mouse Grp94. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P08113 |
| |
| Gene/Protein Identifier: | NP_035761 (RefSeq) |
| |
| Source: | Purified from rabbit serum. |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat
Bovine
|
| |
| Applications: | ICC, IHC (PS), IP, WB
|
| |
| Recommended Dilutions/Conditions: | Immunoprecipitation (1:80)
Western Blot (1:1,000)
Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.
Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| |
| Application Notes: | Detects a band of ~94kDa by Western blot. |
| |
| Purity Detail: | Protein A affinity purified. |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In PBS, pH 7.2, containing 50% glycerol and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| |
| Handling: | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Scientific Background: | Grp94 (Glucose-regulated protein 94) is an abundant resident endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumenal stress protein, which together with cytosolic Hsp90 belongs to the Hsp90 family of molecular chaperones. Grp94 expression is upregulated by stress conditions such as glucose starvation and heat shock, which promote protein misfolding or unfolding. In addition to a homeostatic role in protein folding and assembly, Grp94 can function in the intracellular trafficking of peptides from the extracellular space to the MHC class I antigen processing pathway of antigen presentation cells. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
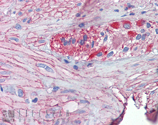
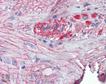
Immunohistochemistry analysis of human small intestine tissue stained with Grp94, pAb at 10µg/ml.
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
CHIP Haploinsufficiency Exacerbates Hepatic Steatosis via Enhanced TXNIP Expression and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Responses: J.H. Han, et al.; Antioxidants
12, 458 (2023),
Abstract;
Improved skeletal muscle fatigue resistance in experimental autoimmune myositis mice following high-intensity interval training: T. Yamdaa, et al.; Arthritis Res. Ther.
24, 156 (2022),
Abstract;
Suppression of ER-stress induction of GRP78 as an anti-neoplastic mechanism of the cardiac glycoside Lanatoside C in pancreatic cancer: Lanatoside C suppresses GRP78 stress inductio: D.P. Ha, et al.; Neoplasia
23, 1213 (2021),
Abstract;
Molecular adaptation to calsequestrin 2 (CASQ2) point mutations leading to catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT): comparative analysis of R33Q and D307H mutants: G. Valle, et al.; J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil.
41, 251 (2020),
Abstract;
Full Text
The HSP90 inhibitor, 17AAG, protects the intestinal stem cell niche and inhibits graft versus host disease development: A.L. Joly, et al.; Oncogene
35, 2842 (2016),
Application(s): Western Blot,
Abstract;
Characterization and Mechanism of Stress-induced Translocation of 78-kilodalton Glucose Regulated Protein (GRP78) to the Cell Surface: Y.L. Tsai, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
290, 8049 (2015),
Application(s): Western Blotting,
Abstract;
Full Text
The molecular chaperone gp96/GRP94 interacts with Toll-like receptors and integrins via its C-terminal hydrophobic domain: S. Wu, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
287, 6735 (2012),
Abstract;
Heat shock protein gp96 is a master chaperone for toll-like receptors and is important in the innate function of macrophages: Z. Li, et al. ; Immunity
26, 215 (2007),
Application(s): WB, IP using mouse & human cell lysates & tissue culture,
Abstract;
Early intraneuronal Abeta deposition in the hippocampus of APP transgenic mice: L.W. Jin, et al. ; Neuroreport
14, 123 (2003),
Application(s): ICC using mouse samples,
Abstract;
Human U251MG glioma cells expressing the membrane form of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (mM-CSF) are killed by human monocytes in vitro and are rejected within immunodeficient mice via paraptosis that is associated with increased expression of three different heat shock proteins: M.R. Jadus, et al. ; Cancer Gene Ther.
10, 411 (2003),
Application(s): IHC using human tissue,
Abstract;
Induction of GRP78 by ischemic preconditioning reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress and prevents delayed neuronal cell death: P.H. Chan, et al. ; J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.
23, 949 (2003),
Application(s): WB, IHC using rat samples,
Abstract;
Overexpression of glucose-regulated protein94 (Grp94) in esophageal adenocarcinomas of a rat surgical model and humans: C.S. Yang, et al. ; Carcinogenesis
23, 123 (2002),
Application(s): IHC, WB using rat & human samples,
Abstract;
Iodoacetate protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic and oxidative injury: involvement of heat-shock proteins and Bcl-2: M. Mattson, et al. ; J. Neurochem.
79, 361 (2001),
Application(s): WB using rat samples,
Abstract;
The C-terminal domain of human grp94 protects the catalytic subunit of protein kinase CK2 (CK2 alpha) against thermal aggregation - role of disulfide bonds: E. Itarte, et al. ; Eur. J. Biochem.
268, 429 (2001),
Application(s): WB using human samples,
Abstract;
A novel human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein, gpUS9, which promotes cell-to-cell spread in polarized epithelial cells, colocalizes with the cytoskeletal proteins E-cadherin and F-actin: L. Pereira, et al. ; J. Virol.
72, 5717 (1998),
Application(s): ICC using canine samples,
Abstract;
Related Products