-
No-transfection required
-
Can be used as a supplement to the Wnt LEADING LIGHT® Wnt Reporter Assay Starter Kit (Prod. No. ENZ-61001)
-
When used in the Wnt LEADING LIGHT® Wnt Reporter Assay Starter Kit, there are many advantages of using this line of products:
-
True end-point detection system
-
High sensitivity (Wnt3a EC50 = 45.9 ng/ml)
-
Excellent reproducibility (Z'-factor of 0.74)
-
High signal-to-noise ratio without the need for Lithium Chloride to boost the signal
-
High-throughput screening applications (including 384-well microplates)
The LEADING LIGHT® Wnt Reporter Cell Line is the basis for a cell-based luciferase activity test suitable for a multi-well plate format, such as 96- or 384-well microplates. The system contains an engineered 3T3 mouse fibroblast cell line, which expresses the firefly luciferase reporter gene under the control of Wnt-responsive promoters (TCF/LEF). The luciferase activity from the reporter gene in this cell line can be up-regulated in a dose-dependent manner upon the addition of exogenous Wnt protein/Wnt agonist or down-regulated by a further addition of a Wnt antagonist to the cell culture medium. This system can be used to elucidate the functions/activities of different Wnt-related ligands such as Wnt, DKK, etc. This system can also be used for screening small molecules and antibodies for their ability to act as Wnt inhibitors or Wnt agonists.
The assay has been used successfully in different assay formats (including HTS applications) to identify several distinct categories of small molecule compounds that modulate the Wnt signaling pathway.
Note: the complete LEADING LIGHT® Wnt Reporter Assay Starter Kit (Prod. No. ENZ-61001) is available.
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Wnt reporter cell line |
| |
| Quantity: | 1ml, 2 x 106 cells |
| |
| Shipping: | Dry Ice |
| |
| Short Term Storage: | -80°C |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | Liquid nitrogen |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Upon receipt, remove the vial of reporter cell line from the box and store in liquid nitrogen. When stored properly, these cells are stable for one year from date received. |
| |
| Scientific Background: | Wnt ligands bind to Frizzled (Fz) and LRP5/6 receptors to trigger a signaling cascade that leads to stabilization of beta-catenin, which can enter into the nucleus to form a complex with T cell transcription factor (TCF/LEF) to activate Wnt target gene expression1. Canonical Wnt signaling is required for embryo-genesis and adult tissue maintenance and is involved in tumorigenesis and development of many human degenerative diseases. Studies relating to Wnt signaling have advanced research in molecular embryology, stem cell biology, tumorigenesis, regenerative medicine, and rational drug discovery. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
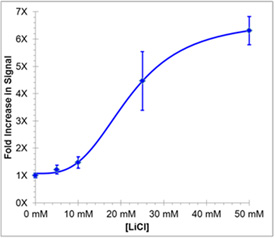
Activation of Wnt reporter gene by LiCl in the Wnt Reporter cell system. Cells were treated with the indicated doses of LiCl. After LiCl treatment, luciferase activity was measured. The chemiluminescence in the LiCl-treated cells increased in a dose-dependent fashion.
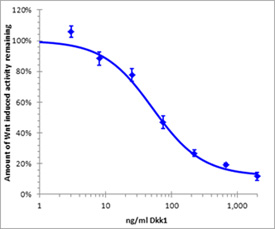
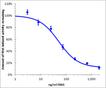
Reporter cells were treated with the indicated doses of Dkk-1 in the presence of 200 ng/mL (in-well) Wnt3a. After Dkk-1 treatment, luciferase activity in the cells was measured. Dkk-1 inhibits Wnt3a-elevated luciferase levels in a dose dependent manner.
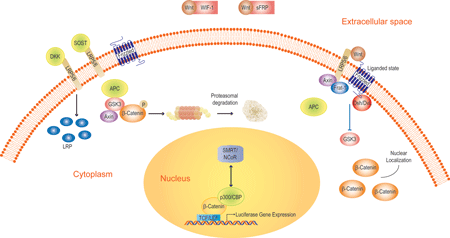
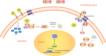
Schematic of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway and its components. Luciferase activity from the reporter gene in the LEADING LIGHT® Wnt reporter cell line can be up- or down-regulated in a dose-dependent manner upon the addition of exogenous Wnt protein/Wnt agonist or Wnt antagonist (Dkk) to the cell culture medium.
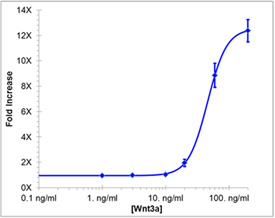
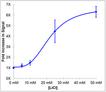
Wnt reporter cells were treated with indicated doses of Wnt3a protein. After Wnt3a treatment, the luciferase activity assay was performed. The chemiluminescence in the Wnt3a-treated cells increased in a dose-dependent manner.
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Ginsenoside Re prevents 3-methyladenine-induced catagen phase acceleration by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in human dermal papilla cells: G. Jeong, et al.; J. Ginseng Res.
47, 440 (2023),
Abstract;
AdipoRon attenuates Wnt signaling by reducing cholesterol-dependent plasma membrane rigidity: M.L. Salinas, et al.; Biophys. J.
118, 885 (2020),
Abstract;
Full Text
Galectin-1 inhibition attenuates profibrotic signaling in hypoxia-induced pulmonary fibrosis: J.J. Kathiriya, et al.; Cell Death Discov.
3, 17010 (2017),
Abstract;
Full Text
Noncanonical WNT-5A signaling impairs endogenous lung repair in COPD: H.A. Baarsma, et al.; J. Exp. Med.
214, 143 (2017),
Abstract;
Full Text
ARID3B directly regulates ovarian cancer promoting genes: A. Bobbs, et al.; PLoS One
10, e0131961 (2015),
Abstract;
Full Text
Cardiomyocyte differentiation of pluripotent stem cells with SB203580 analogues correlates with Wnt pathway CK1 inhibition independent of p38 MAPK signaling: F. Laco, et al.; J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.
80, 56 (2015),
Abstract;
Chemical and genetic evidence for the involvement of Wnt antagonist Dickkopf2 in regulation of glucose metabolism: X. Li, et al.; PNAS
109, 11402 (2012),
Abstract;
Full Text
General Literature References
Histone deacetylase is a target of valproic acid-mediated cellular differentiation: N. Gurvich et al.; Cancer. Res.
64, 1079 (2004),
Abstract;
Phosphorus-based SAHA analogues as histone deacetylase inhibitors: G.V. Kapustin et al.; Org. Lett.
5, 3053 (2003),
Abstract;
Phosphorus-based SAHA analogues as histone deacetylase inhibitors: G.V. Kapustin et al.; Org. Lett.
5, 3053 (2003),
Abstract;
Inhibition of silencing and accelerated aging by nicotinamide, a putative negative regulator of yeast sir2 and human SIRT1: K.J. Bitterman et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
277, 45099 (2002),
Abstract;
Cloning and characterization of a histone deacetylase, HDAC9: X. Zhou et al.; PNAS
98, 10572 (2001),
Abstract;
Coupling of histone deacetylation to NAD breakdown by the yeast silencing protein Sir2: Evidence for acetyl transfer from substrate to an NAD breakdown product: J.C. Tanny et al.; PNAS
98, 415 (2001),
Abstract;
Identification of a class of small molecule inhibitors of the sirtuin family of NAD-dependent deacetylases by phenotypic screening: C.M. Groezigner et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
276, 38837 (2001),
Abstract;
A phylogenetically conserved NAD+-dependent protein deacetylase activity in the Sir2 protein family: J.S. Smith et al.; PNAS
97, 6658 (2000),
Abstract;
Acetylation and chromosomal functions: W.L. Cheung et al.; Curr. Opin. Cell Biol.
12, 326 (2000),
Abstract;
Cloning and characterization of a novel human class I histone deacetylase that functions as a transcription repressor: E. Hu et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
275, 15254 (2000),
Abstract;
Histone deacetylases: silencers for hire: H.H. Ng et al.; Trends Biochem. Sci.
25, 121 (2000),
Abstract;
Isolation of a novel histone deacetylase reveals that class I and class II deacetylases promote SMRT-mediated repression: H.-Y. Kao et al.; Genes Dev.
14, 55 (2000),
Abstract;
Role of NAD(+) in the deacetylase activity of the SIR2-like proteins: J. Landry et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.
278, 685 (2000),
Abstract;
Silent information regulator 2 family of NAD- dependent histone/protein deacetylases generates a unique product, 1-O-acetyl-ADP-ribose: K.G. Tanner et al.; PNAS
97, 14178 (2000),
Abstract;
The language of covalent histone modifications: B.D. Strahl et al.; Nature
403, 41 (2000),
Abstract;
Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase: S. Imai et al.; Nature
403, 795 (2000),
Abstract;
A new family of human histone deacetylases related to Saccharomyces cerevisiae HDA1p: W. Fischle et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
274, 11713 (1999),
Abstract;
HDAC4, a human histone deacetylase related to yeast HDA1, is a transcriptional corepressor: P. A. Wade et al.; Mol. Cell Biol.
19, 7816 (1999),
Abstract;
Identification of a new family of higher eukaryotic histone deacetylases. Coordinate expression of differentiation-dependent chromatin modifiers: A. Verdel et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
274, 2440 (1999),
Abstract;
Three proteins define a class of human histone deacetylases related to yeast Hda1p: C.M. Groezigner et al.; PNAS
96, 4868 (1999),
Abstract;
SAP30, a novel protein conserved between human and yeast, is a component of a histone deacetylase complex: Y. Zhang et al.; Mol. Cell
1, 1021 (1998),
Abstract;
Targeted recruitment of the Sin3-Rpd3 histone deacetylase complex generates a highly localized domain of repressed chromatin in vivo: D. Kadosh et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol.
18, 5121 (1998),
Abstract;
Transcriptional repression by UME6 involves deacetylation of lysine 5 of histone H4 by RPD3: S.E.C. Rundlett et al.; Nature
392, 831 (1998),
Abstract;
Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription: M. Grunstein; Nature
389, 349 (1997),
Abstract;
Isolation and characterization of cDNAs corresponding to an additional member of the human histone deacetylase gene family: W. M. Yang et al.; J Biol Chem
272, 28001 (1997),
Abstract;
A mammalian histone deacetylase related to the yeast transcriptional regulator Rpd3p: J. Taunton et al.; Science
272, 408 (1996),
Abstract;
Transcriptional repression by YY1 is mediated by interaction with a mammalian homolog of the yeast global regulator RPD3: W.M. Yang et al.; PNAS
93, 12845 (1996),
Abstract;
Enzymatic deacetylation of histone: A. Inoue et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.
36, 146 (1969),
Abstract;
Related Products