Replaces Prod. #: ALX-380-012
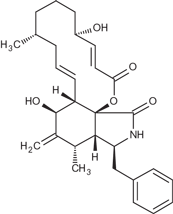
Cytochalasin B is a cell-permeable fungal toxin which binds to the barbed end of actin filaments inhibiting both the association and dissociation of subunits. It causes the disruption of actin filaments and inhibition of actin polymerization. It also inhibits monosaccharide transport across cell membranes. inhibits glucose transport and platelet aggregation. Blocks adenosine-induced apoptotic body formation without affecting activation of endogenous ADP-ribosylation in leukemia HL-60 cells.
Product Details
| Formula: | C29H37NO5 |
| |
| MW: | 479.6 |
| |
| Source: | Isolated from Drechslera dematoidea |
| |
| CAS: | 14930-96-2 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC, TLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to off-white solid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in methanol or DMSO (20mg/ml). |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
CRM1 promotes capsid disassembly and nuclear envelope 2 translocation of adenovirus independently of its export function: F. Lagadec, et al.; J. Virol.
96, e0127321 (2022),
Abstract;
Discovery of a specific inhibitor of human GLUT5 by virtual screening and in vitro transport evaluation: A.M. George Thompson, et al.; Sci. Rep.
6, 24240 (2016),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
The inhibition of GLUT1 glucose transport and cytochalasin B binding activity by tricyclic antidepressants: H.B. Pinkofsky et al.; Life. Sci.
66, 271 (2000),
Abstract;
Cytochalasin B may shorten actin filaments by a mechanism independent of barbed end capping: P.A. Theodoropoulos et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol.
47, 1875 (1994),
Abstract;
Effect of cytochalasin B on glucose uptake, utilization, oxidation and insulinotropic action in tumoral insulin-producing cells: W.J. Malaisse; Cell. Biochem. Funct.
5, 183 (1987),
Abstract;
Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin: J.A. Cooper; J. Cell. Biol.
105, 1473 (1987),
Abstract;
Effects of cytochalasin B on endocytosis and exocytosis: P. Davies & A.C. Allison; Front. Biol.
46, 143 (1978),
Abstract;
Cytochalasin B: effects on cell morphology, cell adhesion, and mucopolysaccharide synthesis (cultured cells-contractile microfilaments-glycoproteins-embryonic cells-sorting-out): J.W. Sanger & H. Holtzer; PNAS
69, 253 (1972),
Abstract;
Cytochalasin B: inhibition of glucose and glucosamine transport: R.D. Ebstensen & P.G. Plagemann; PNAS
69, 1430 (1972),
Abstract;