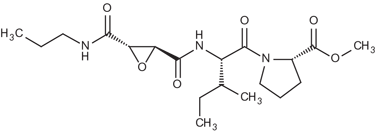
Potent and selective irreversible cell permeable cathepsin B inhibitor. Methyl ester (Me) is hydrolyzed by intracellular esterases releasing the active inhibitor. Prevents death of CA1 neurons after ischemia following IV delivery after the ischemic insult. In isolated rat osteoclasts it inhibited bone resorption with a maximal effect at 50 µM. This product is only suitable for in vivo and whole cell experiments. The free acid form must be used for in vitro experiments. Can be used to discriminate between cathepsin B and L/S forms.
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | N-(L-3-trans-Propylcarbonyl-oxirane-2-carbonyl)-L-isoleucyl-L-proline methyl ester |
| |
| Sequence: | N-(L-3-trans-Propylcarbonyl-oxirane-2-carbonyl)-L-isoleucyl-L-proline methyl ester |
| |
| Formula: | C19H31N3O6 |
| |
| MW: | 397.5 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | White solid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DMSO. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Lysosomal cathepsins act in concert with Gasdermin-D during NAIP/NLRC4-dependent IL-1β secretion: L. M. Branco, et al.; Cell Death Dis.
13, 1029 (2022),
Abstract;
Cathepsin B Localizes in the Caveolae and Participates in the Proteolytic Cascade in Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Potential New Drug Target for the Treatment of Glaucoma: A. Nettesheim, et al.; J. Clin. Med.
10, 78 (2020),
Abstract;
Lysosomal dysfunction and autophagy blockade contribute to MDMA-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: I.H. Li, et al.; Chem. Res. Toxicol.
33, 903 (2020),
Abstract;
Role of Autophagy in Von Willebrand Factor Secretion by Endothelial Cells and in the In Vivo Thrombin-Antithrombin Complex Formation Promoted by the HIV-1 Matrix Protein p17: A. Bugatti, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci.
21, 2022 (2020),
Abstract;
Full Text
The vacuolar-type ATPase inhibitor archazolid increases tumor cell adhesion to endothelial cells by accumulating extracellular collagen: B. Luong, et al.; PLoS One
13, e0203053 (2018),
Abstract;
Full Text
Neutrophil and Alveolar Macrophage-Mediated Innate Immune Control of Legionella pneumophila Lung Infection via TNF and ROS: P. Ziltener, et al.; PLoS One
12, e1005591 (2016),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
ATG16L1 deficiency in macrophages drives clearance of uropathogenic E. coli in an IL-1β-dependent manner: J.W. Symington, et al.; Mucosal Immunol.
8, 1388 (2015),
Application(s): Cell Culture, ELISA,
Abstract;
Synthesis of marmycin A and investigation into its cellular activity: T. Cañeque, et al.; Nat. Chem.
7, 744 (2015),
Application(s): Cell Culture,
Abstract;
An intracellular form of cathepsin B contributes to invasiveness in cancer: A, M. Szpaderska et al.; Cancer Res.
61, 3493 (2001),
Abstract;
Fluorometric microassays for the determination of cathepsin L and cathepsin S activities in tissue extracts: B. Werle et al.; Biol. Chem.
380, 1109 (1999),
Abstract;
Postictal blockade of ischemic hippocampal neuronal death in primates using selective cathepsin inhibitors: K. Tsuchiya et al.; Exp. Neurol.
155, 187 (1999),
Abstract;
Inhibition of bone resorption by selective inactivators of cysteine proteinases: P. A. Hill et al.; J. Cell. Biochem.
56, 118 (1994),
Abstract;