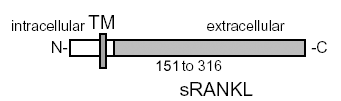Product Details
| Alternative Name: | TRANCE, OPGL, ODF, TNFSF 11, CD254 |
| |
| MW: | ~18kDa (non-glycosylated), ~28kDa (glycosylated) (SDS-PAGE). |
| |
| Source: | Produced in HEK 293 cells. The extracellular domain of human RANKL (aa 152-317) is fused at the N-terminus to a linker peptide (6 aa) and a FLAG®-tag. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | O14788 |
| |
| Concentration: | 0.1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| |
| Purity: | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) |
| |
| Endotoxin Content: | <0.1EU/µg purified protein (LAL test; Associates of Cape Cod). |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human, Mouse
|
| |
| Specificity: | Binds to human and mouse RANK. |
| |
| Applications: | ELISA
|
| |
| Application Notes: | ELISA: binds to RANK receptor. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in water. |
| |
| Reconstitution: | Reconstitute with 100µl sterile water. Further dilutions should be made with medium containing 5% fetal calf serum or a carrier protein. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| |
| Handling: | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| |
| Scientific Background: | RANK ligand (RANKL), also called TRANCE, OPGL and ODF, is a member of the TNF family that is expressed in activated T cells, lymph nodes and in stromal cell lines. RANKL (TRANCE) interacts with its receptor RANK expressed on mature dendritic cells (DC) and mature osteoclasts, leading to the inhibition of apoptosis, probably through the upregulation of bcl-x. RANKL is, therefore, a useful tool for enhancing DC and osteoclast survival and activity. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is a potent inhibitor of RANKL.
Historical data has shown that the biological activity of RANKL supports the survival of dendritic cells and osteoclasts. |
| |
| Technical Info/Product Notes: | FLAG is a registered trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
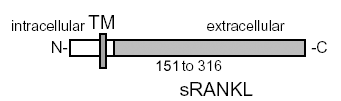
Figure 1: Schematic structure of human rhsRANKL (peptide, aa. 151-316).
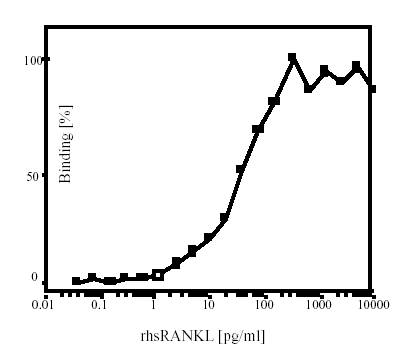
Figure 2: Binding of rhsRANKL to Osteoprotegerin. Recombinant, human sRANKL binds to Osteoprotegerin:Fc (see Prod. No.
ALX-522-007).
Method: Ligand binding assay: 96 well ELISA plates were coated O/N with 50 ng OPG-Fc (Prod. No.
ALX-522-007) per well. After a blocking step, the indicated concentrations of Flag-tagged RANKL were added for 1 hour. Bound ligand was revealed with an anti-FLAG antibody (Prod. No.
ALX-804-034) at 1 µ/ml for 30 minutes, followed by a rabbit anti-mouse IgG-HRP at 1/1000 dilution for 30 minutes. OPD was used as a substrate for the peroxidase. Absorbance was measured at 490 nm in an ELISA reader."
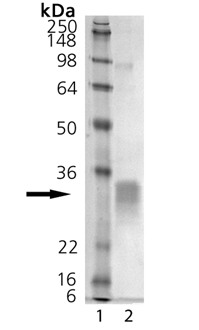
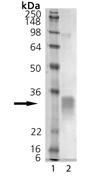
SDS-PAGE Analysis of RANKL (soluble) (human), (recombinant). Lane 1: MW Marker, Lane 2: 1µg.
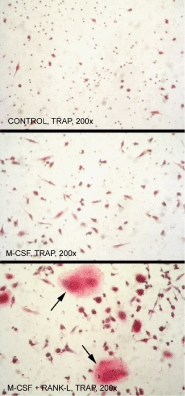
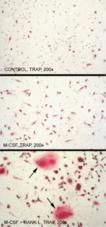
Figure 3: Mononuclear cells differentiate into Osteoclasts in the presence of M-CSF and RANKL, Soluble (human) (recombinant) (
ALX-522-012).
Method: Human CD14+ mononuclear cells isolated from adult peripheral blood were cultured in control medium (upper panel), in 25ng/ml M-CSF (middle panel), or in 25ng/ml M-CSF plus 50ng/ml RANKL (lower panel). Osteoclasts were identified as Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAP)-positive multinucleated cells. Osteoclasts were detected exclusively in presence of RANKL and in these culture conditions (M-CSF + RANKL), cells fused and generated multinucleated dark red TRAP-positive cells (arrows). Nuclei were stained with haematoxylin. Original magnification: 200x.
Picture courtesy of V.Kindler and D.Suvà, University of Geneva."
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
An in vitro model for discovery of osteoclast specific biomarkers towards identification of racehorses at risk for catastrophic fractures: G. Malek, et al.; Equine Vet. J.
1111, evj.13600 (2022),
Abstract;
Synthetic ligands of death receptor 5 display a cell-selective agonistic effect at different oligomerization levels: J. Beyrath, et al.; Oncotarget
7, 64942 (2016),
Abstract;
Full Text
Porous gelatin/tricalcium phosphate/genipin composites containing lumbrokinase for bone repair: Y.T. Fu, et al.; Bone
78, 15 (2015),
Abstract;
Earthworm (Pheretima aspergillum) extract stimulates osteoblast activity and inhibits osteoclast differentiation: Y.T. Fu, et al.; BMC Complement. Altern. Med.
14, 440 (2014),
Abstract;
Full Text
XPO1/CRM1-selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINE) reduce tumor spreading and improve overall survival in preclinical models of prostate cancer (PCa): G.L. Gravina, et al.; J. Hematol. Oncol.
7, 46 (2014),
Abstract;
Full Text
R848, a toll-like receptor 7 agonist, inhibits osteoclast differentiation but not survival or bone-resorbing function of mature osteoclasts: A. Miyamoto, et al.; Cytotechnology
64, 331 (2012),
Abstract;
Full Text
Crosstalk of osteoblast and osteoclast precursors on mineralized collagen--towards an in vitro model for bone remodeling: A. Bernhardt, et al.; J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A
95, 848 (2010),
Abstract;
Icariin inhibits the osteoclast formation induced by RANKL and macrophage-colony stimulating factor in mouse bone marrow culture: K.M. Chen, et al.; Pharmazie
62, 388 (2007),
Abstract;
A novel in vivo role for osteoprotegerin ligand in activation of monocyte effector function and inflammatory response: D. Seshasayee, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
279, 30202 (2004),
Abstract;
Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by the Proteasome Inhibitor PS-341 in Hodgkin Disease Cell Lines Is Independent of Inhibitor of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Mutations or Activation of the CD30, CD40, and RANK Receptors: B. Zheng, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res.
10, 3207 (2004),
Abstract;
Suppression of IL-12 Production by Soluble CD40 Ligand: Evidence for Involvement of the p44/42 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway: M. Wittmann, et al.; J. Immunol.
168, 3793 (2002),
Abstract;
Functional expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB in Hodgkin disease cell lines: P. Fiumara, et al.; Blood
98, 2784 (2001),
Abstract;
Full Text
Receptor activator of NF-κB and osteoprotegerin expression by human microvascular endothelial cells, regulation by inflammatory cytokines, and role in human osteoclastogenesis: P. Collin-Osdoby, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
276, 20659 (2001),
Abstract;
Full Text
General Literature References
Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL: H. Yasuda, et al.; PNAS
95, 3597 (1998),
Abstract;
Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation: D.L. Lacey, et al.; Cell
93, 165 (1998),
Abstract;
A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function: D.M. Anderson, et al.; Nature
390, 175 (1997),
Abstract;
TRANCE (tumor necrosis factor [TNF]-related activation-induced cytokine), a new TNF family member predominantly expressed in T cells, is a dendritic cell-specific survival factor: B.R. Wong, et al.; J. Exp. Med.
186, 2075 (1997),
Abstract;