Replaces Prod. #: BML-EI291
Naturally occurring polyphenolic compound with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.Inhibits several complement-dependent inflammatory processes via inhibition of the C5 convertase. Anticarcinogenic. Inhibitor of lipid peroxidation, TCR-induced T cell activation and proliferation.
Product Details
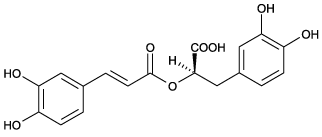
| Alternative Name: | (R)-α-[[3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2E-propenyl]oxy]-3,4-dihydroxy-benzenepropanoic acid |
| |
| Formula: | C18H16O8 |
| |
| MW: | 360.3 |
| |
| Source: | Isolated from Rosmarinus officinalis. |
| |
| CAS: | 537-15-5, 20283-92-5 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥97% (HPLC) |
| |
| Identity: | Determined by NMR. |
| |
| Appearance: | White to off-white powder. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in 100% ethanol, DMSO or dimethyl formamide; also soluble in PBS. |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | Ambient |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Rosmarinic acid inhibits angiogenesis and its mechanism of action in vitro: S.S. Huang & R.L. Zheng; Cancer Lett.
239, 271 (2006),
Abstract;
Effects of rosmarinic acid against aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin-A-induced cell damage in a human hepatoma cell line (Hep G2): C. Renzulli, et al.; J. Appl. Toxicol.
24, 289 (2004),
Abstract;
Rosmarinic acid inhibits epidermal inflammatory responses: anticarcinogenic effect of Perilla frutescens extract in the murine two-stage skin model: N. Osakabe, et al.; Carcinogenesis
25, 549 (2004),
Abstract;
Rosmarinic acid inhibits Ca2+-dependent pathways of T-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling by inhibiting the PLC-gamma 1 and Itk activity: M.A. Kang, et al.; Blood
101, 3534 (2003),
Abstract;
Rosmarinic acid inhibits TCR-induced T cell activation and proliferation in an Lck-dependent manner: J. Won, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol.
33, 870 (2003),
Abstract;
Metabolism of rosmarinic acid in rats: T. Nakazawa & K. Ohsawa; J. Nat. Prod.
61, 993 (1998),
Abstract;
Protective action of seven natural phenolic compounds against peroxidative damage to biomembranes: G.T. Liu, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol.
43, 147 (1992),
Abstract;
The inhibitory effect of rosmarinic acid on complement involves the C5 convertase: P.W. Peake et al.; Int. J. Immunopharmacol.
13, 853 (1991),
Abstract;
Studies on the activities of tannins and related compounds, X. Effects of caffeetannins and related compounds on arachidonate metabolism in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: Y. Kimura, et al.; J. Nat. Prod.
50, 392 (1987),
Abstract;
Complement-dependent stimulation of prostacyclin biosynthesis: inhibition by rosmarinic acid: M. Rampart, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol.
35, 1397 (1986),
Abstract;
Modification of endotoxin-induced haemodynamic and haematological changes in the rabbit by methylprednisolone, F(ab')2 fragments and rosmarinic acid: H. Bult, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol.
84, 317 (1985),
Abstract;