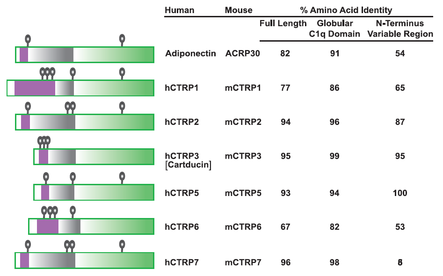
Structure of adiponectin/ACRP30 paralogs CTRPs 1–7. The predicted amino acid sequences of all of the CTRPs share a similar modular organization to adiponectin and consist of four distinct domains; a signal peptide (white), a short variable region (purple), a collagenous domain with various length of Gly-X-Y repeats (grey), and a C-terminal globular domain homologous to complement C1q (green). indicates cysteine residues; cysteine residues in the signal peptides are not shown because they are not part of the mature proteins. Adapted from: A family of Acrp30/adiponectin structural and functional paralogs. G. W. Wong, et al.; PNAS101, 10302 (2004).