The NUCLEAR-ID® Blue/Red cell viability reagent (GFP-CERTIFIED®) (Prod. No. ENZ-53005) is a mixture of a blue fluorescent cell-permeable nucleic acid dye and a red fluorescent cell-impermeable nucleic acid dye that is suited for staining dead nuclei. The staining pattern arising from the simultaneous combination of these two dyes permits determination of live and dead cell populations by fluorescence/confocal microscopy. The reagent, supplied as a 1000x solution, is sufficient for 1000 microscopy assays. The single-tube format makes this cell viability reagent easy to use. It leaves the cytoplasm unstained, potentially allowing visualization of other cell markers. This reagent is specificially designed for use with GFP-expressing cell lines.
Product Details
| Quantity: | 100μl (for 1000 microscopy assays). |
| |
| Purity: | ≥93% (HPLC) |
| |
| Applications: | Flow Cytometry, Fluorescence microscopy, Fluorescent detection
|
| |
| Shipping: | Dry Ice |
| |
| Short Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -80°C |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| |
| Technical Info/Product Notes: | Application Notes:
Use of 3D Cultured Human iPSC-Derived Hepatocytes for Long-Term Hepatotoxicity Studies
Image-Based Analysis of a Human Neurosphere Stem Cell Model for the Evaluation of Potential Neurotoxicants
Multiplexed Assay for IL-6 Secretion and Cell Viability Using an Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cell Line
Validation of a Novel Tumoroid-Based Cell Culture Model to Perform 3D in vitro Cell Signaling Analyses
Wavelength Maxima
Live (Blue): Excitation: 350nm; Emission: 461nm
Dead (Red): Excitation: 571, 619nm; Emission: 639nm
NUCLEAR-ID® Blue/Red cell viability reagent is a member of the CELLESTIAL® product line, reagents and assay kits comprising fluorescent molecular probes that have been extensively benchmarked for live cell analysis applications. CELLESTIAL® reagents and kits are optimal for use in demanding imaging applications, such as confocal microscopy, flow cytometry and HCS, where consistency and reproducibility are required. |
| |
| Protocol: | Wide Field Fluorescence/Confocal Microscopy
Reagent Preparation:
Mix 1μL of NUCLEAR-ID® Blue/Red Cell Viability Reagent in 1 mL of buffer of choice. This volume is sufficient for 10 assays and may be scaled according to need.
Staining Adherent cells:- Grow cells directly onto glass slides or polystyrene tissue culture plates until ~80% confluent via standard tissue culture practices.
- Remove growth media.
- Dispense the freshly diluted staining solution in a volume sufficient for covering the cell monolayer.
- Protect samples from light and incubate for 30 minutes at 37°C.
- Remove the excess staining solution and, if necessary, add a few drops of buffer to prevent the cells from drying out.
- Cover cells with a glass cover slip and observe under a fluorescence/confocal microscope with a dual filter set for DAPI (Ex/Em: 350/470nm) and Texas Red (Ex/Em: 540/605 nm).
Staining Non-Adherent Cells:- Grow cells via standard tissue culture practices.
- Collect about 1 x 105 cells. Centrifuge at 500 x g for 5 minutes. Remove supernatant.
- Re-suspend cells in a volume of the freshly diluted staining solution sufficient for covering the cell pellet.
- Protect samples from light and incubate for 30 minutes at 37°C.
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 5 minutes. Remove supernatant.
- Re-suspend cells in 100µL buffer
- Plate 10-15µL of cells on a glass slide.
- Cover cells with a glass cover slip and observe under a fluorescence/confocal microscope with a dual filter set for DAPI (Ex/Em: 350/470nm) and Texas Red (Ex/Em: 540/605 nm).
|
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
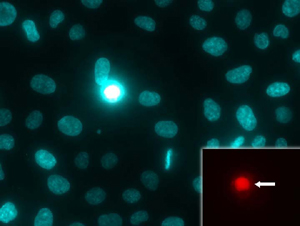
Figure 1: NUCLEAR-ID® Blue/Red dye is detected as blue-stained nuclei in live cells and fluorescent-red nuclei in dead cells (inset, arrow).
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Hyperexcitability and pharmacological responsiveness of cortical neurons derived from human iPSCs carrying epilepsy-associated sodium channel Nav1. 2-L1342P genetic variant: Z. Que, et al.; J. Neurosci.
41, 10194 (2021),
Abstract;
Alginate/Pluronic F127-based encapsulation supports viability and functionality of human dental pulp stem cell-derived insulin-producing cells: S. Kuncorojakti, et al.; J. Biol. Eng.
14, 23 (2020),
Abstract;
Full Text
Hydrogen sulfide inhibits calcification of heart valves; implications for calcific aortic valve disease: K.E. Sikura, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol.
177, 793 (2020),
Abstract;
Full Text
Targeting N-myristoylation for therapy of B-cell lymphomas: E. Beauchamp, et al.; Nat. Commun.
11, 5348 (2020),
Abstract;
Full Text
Tumour necrosis factor induces increased production of extracellular amyloid-β- and α-synuclein-containing aggregates by human Alzheimer's disease neurons: D.R. Whiten, et al.; Brain Commun.
2, fcaa146 (2020),
Abstract;
Full Text
Polyanionic carbosilane dendrimers as a new adjuvant in combination with latency reversal agents for HIV treatment: I. Relano-Rodriguez, et al.; J. Nanobiotechnology
17, 69 (2019),
Abstract;
Full Text
Potential role of H-ferritin in mitigating valvular mineralization: K.E. Sikura, et al.; Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol.
39, 413 (2019),
Application(s): Confocal microscopy using primary cells from human aortic valves,
Abstract;
Epigenetic modifiers promote mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative metabolism leading to enhanced differentiation of neuroprogenitor cells: M. Uittenbogaard, et al.; Cell Death Dis.
9, 360 (2018),
Abstract;
Full Text
The effect of Hypomyces perniciosus on the mycelia and basidiomes of Agaricus bisporus: C. Zhang, et al.; Microbiology
163, 1273 (2017),
Abstract;
An easy-to-use polystyrene microchip-based cell culture system: H. Tazawa, et al.; Anal. Sci.
32, 349 (2016),
Abstract;
Mechanical properties and biocompatibility of the sputtered Ti doped hydroxyapatite: A. Vladescu, et al.; J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater.
63, 314 (2016),
Application(s): Viability of MG63 human osteosarcoma cells analyzed under fluorescence microscope,
Abstract;
Nav1.7-A1632G mutation from a family with inherited erythromelalgia: enhanced firing of dorsal root ganglia neurons evoked by thermal stimuli: Y. Yang, et al.; J. Neurosci.
36, 7511 (2016),
Abstract;
Suppression of Atherosclerosis by Synthetic REV-ERB Agonist: S. Sitaula, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.
460, 566 (2015),
Application(s): Assay,
Abstract;
Phenotypic switch in blood: effects of pro-inflammatory cytokines on breast cancer cell aggregation and adhesion: Y. Geng, et al.; PLoS One
8, e54959 (2013),
Application(s): Breast cancer cell viability observed by confocal microscopy,
Abstract;
Full Text
General Literature References
Constitutive expression of the machinery for programmed cell death: M. Weil, et al.; J. Cell Biol.
133, 1053 (1996),
Abstract;
Principles and Methods of Toxicology, Third Edition: A.W. Hayes, Ed.; Raven Press 1231 (1994), Book,
Related Products















