-
Simultaneous staining of both the nucleolus and the nucleus in live cells
-
High resistance to photobleaching and concentration quenching, ensuring strong, consistent fluorescence signal, even after extended viewing periods
-
Validated for utility in live cell imaging applications, demonstrating appropriate response to treatment with well characterized nucleolus-perturbation agents
-
Stringently manufactured, to control and eliminate non-specific assay artifacts
Enzo Life Sciences’ TOTAL-NUCLEAR-ID® Green/Red Nucleolar/Nuclear Detection Kit contains two proprietary dyes suitable for simultaneous live-cell staining of nucleoli and nuclei. The dyes allow examination of nucleolar dynamic changes in intracellular distribution, trafficking and localization arising from biological processes such as the cell cycle and ribosome biogenesis. The kit is compatible with most fluorescence detection systems, including conventional and confocal fluorescence microscopes, as well as High Content Screening (HCS) platforms. This kit is specifically designed for visualizing nucleoli and nuclei in living cells. A control nucleolus perturbation agent, actinomycin D, is provided for monitoring changes in nucleolar dynamics. Potential applications for this kit include monitoring impaired ribosome biogenesis, inhibition transcription, cell cycle dynamics and cellular stress, as well as the distribution, trafficking and dynamics of nucleolar proteins, the distribution of viral proteins, and potentially as an aid in identifying cancer cells.

Absorption and emission spectra of A) NUCLEOLAR-ID® Green Detection Reagent and B) NUCLEAR-ID® Red Detection Reagent.

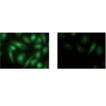
Cells stained with NUCLEOLAR-ID® Green Detection Reagent show maximal fluorescence signal within the nucleoli, and faint fluorescence throughout the nucleus and cytoplasm (A). When the cells are treated with low doses of actinomycin D, loss of nucleolar staining is observed (B). Counterstaining with NUCLEAR-ID® Red Detection Reagent facilitates highlighting the nucleoli relative to the weak cytoplasmic staining.
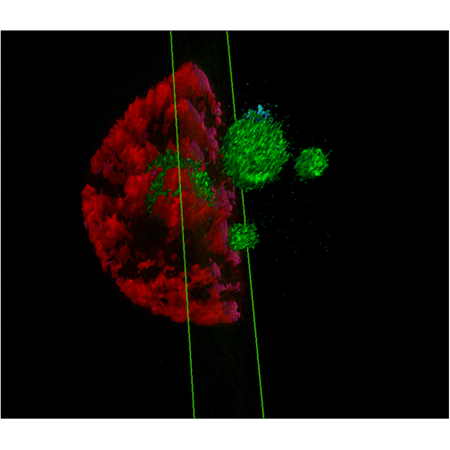
3D reconstruction of nucleus stained red and nucleolus stained green in U2OS cells.
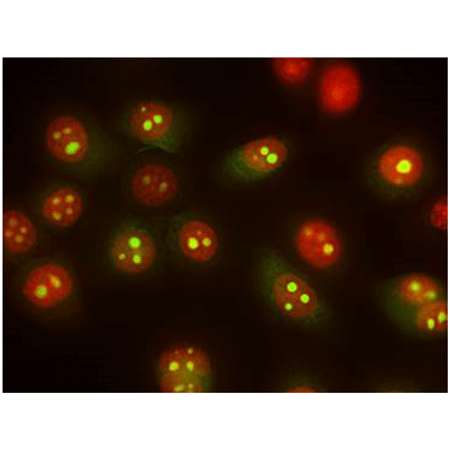
Live U2OS cells, stained with TOTAL-NUCLEAR-ID® Green/Red Nucleolar/ Nuclear Detection Kit demonstrates staining of the nucleus (red) and nucleolus (yellow-green) via fluorescence microscopy. As an RNA stain, NUCLEOLAR-ID® Green dye does display some cytoplasmic staining as well, but NUCLEAR-ID® Red dye facilitates unambiguous identification of the nucleoli as green fluorescence signal within the confines of the highlighted red nuclear fluorescence signal.
Please mouse over
Product Details
| Applications: | Fluorescence microscopy, Fluorescent detection
|
| |
| Application Notes: | For visualizing nucleoli and nuclei simultaneously in living cells. |
| |
| Quality Control: | A sample from each lot of TOTAL-NUCLEAR-ID® Green/ Red Nucleolus/Nucleus Detection Kit is used to stain HeLa cells using the procedures described in the user manual. Cells stained with NUCLEOLAR-ID® Green Detection Reagent show maximal fluorescence signal within the nucleoli, with only faint fluorescence throughout the nucleus and cytoplasm. NUCLEAR-ID® Red Detection Reagent maximally stains the DNA in the cell nucleus. Cells induced by actinomycin D show reduction of nucleolar signal. |
| |
| Quantity: | 500 assays |
| |
| Use/Stability: | With proper storage, the kit components are stable up to the date noted on the product label. Store kit at -20°C in a non-frost free freezer, or -80°C for longer term storage. |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| |
| Shipping: | Dry Ice |
| |
| Short Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -80°C |
| |
| Contents: | NUCLEOLAR-ID® Green Detection Reagent, 50 µL
NUCLEAR-ID® Red Detection Reagent, 50 µL
Actinomycin D Control, 125 µg
10X Assay Buffer, 15 mL |
| |
| Technical Info/Product Notes: | The TOTAL-NUCLEAR-ID® green/red nucleolar/nuclear detection kit is a member of the CELLESTIAL® product line, reagents and assay kits comprising fluorescent molecular probes that have been extensively benchmarked for live cell analysis applications. CELLESTIAL® reagents and kits are optimal for use in demanding imaging applications, such as confocal microscopy, flow cytometry and HCS, where consistency and reproducibility are required. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Product Literature References
Guanidinylated bioresponsive poly(amido amine)s designed for intranuclear gene delivery: J. Yu, et al.; Int. J. Nanomedicine
11, 4011 (2016),
Application(s): Confocal microscopy using MCF7 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Dose-dependent role of the cohesin complex in normal and malignant hematopoiesis: A.D. Viny, et al.; J. Exp. Med.
212, 1819 (2015),
Application(s): Confocal microscopy,
Abstract;
Full Text
Small-molecule multi-targeted kinase inhibitor RGB-286638 triggers P53-dependent and -independent anti-multiple myeloma activity through inhibition of transcriptional CDKs: D. Cirstea, et al.; Leukemia
27, 2366 (2013),
Application(s): Nucleolar segregation analysis by immunofluorescence,
Abstract;
Mismatch in mechanical and adhesive properties induces pulsating cancer cell migration in epithelial monolayer: M.H. Lee, et al.; Biophys. J.
102, 2731 (2012),
Application(s): Detection of nuclei and nucleoli in breast cell lines using fluorescence microscopy,
Abstract;
Full Text
AFM stiffness nanotomography of normal, metaplastic and dysplastic human esophageal cells: A. Fuhrmann, et al.; Phys. Biol.
8, 015007 (2011),
Application(s): Fluorescence lifetime imaging of normal and dysplasic esophageal cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Strategies of actin reorganisation in plant cells: A.P. Smertenko, et al.; J. Cell Sci.
123, 3019 (2010),
Application(s): Staining of plant cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
General Literature References
Nucleolus: the fascinating nuclear body: V. Sirri, et al.; Histochem. Cell. Biol.
129, 13 (2008),
Abstract;
Regulators of nucleolar functions: D. Hernandez-Verdun & P. Roussel; Prog. Cell Cycle Res.
5, 301 (2003),
Abstract;
Immunocytochemical localization of nucleophosmin and RH-II/Gu protein in nucleoli of HeLa cells after treatment with actinomycin : K. Smetana, et al.; Acta Histochem.
103, 325 (2001),
Abstract;
Related Products