Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Apo-2L, TNFSF 10, CD253 |
| |
| MW: | ~23kDa |
| |
| Source: | Produced in E. coli. Human TRAIL (aa 114-281) is fused to a His-tag. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P50591 |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In PBS, containing 10% glycerol and 0.1mM DTT. |
| |
| Purity: | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| |
| Purity Detail: | Purified by multi-step chromatography. |
| |
| Endotoxin Content: | <0.1 EU/µg TRAIL, determined using chromogenic Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) test. |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human, Mouse
|
| |
| Specificity: | Binds to human and mouse TRAIL receptors and human osteoprotegerin (OPG). |
| |
| Biological Activity: | Induces apoptosis in U937 cells at 1µg/ml, within 5 hours. At 0.5-2.0µg/ml, induces apoptosis in various thyroid carcinoma lines within 18 hours. User must determine optimal concentrations and time course for induction. Please note that this protein does not require a cross-linking enhancer to exhibit this potent activity. |
| |
| Shipping: | Dry Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -80°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | When stored at -80°C, this protein is stable at the concentration supplied, in its current storage buffer. Procedures such as dilution of the protein, followed by refreezing, could lead to loss of activity. |
| |
| Handling: | After initial defrost, aliquot product into individual tubes and refreeze at -70°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| |
| Scientific Background: | TRAIL, also called Apo2L, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor family (TNF). In contrast to other family members such as TNFa/TNFR1 and FasL/Fas, TRAIL and its receptors DR4 and DR5 are widely expressed in many human tissues. TRAIL activates rapid apoptosis in many transformed cell lines but not in normal tissues, even though TRAIL and its receptors DR4 and DR5 are expressed on both cell types. A glycophospholipid-anchored cell surface protein designated decoy receptor 1 (DcR1 or TRID) acts as a decoy to inhibit TRAIL signaling. Thus, TRAIL and its signaling pathways may have direct applications in selective tumor cell death and cancer research. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
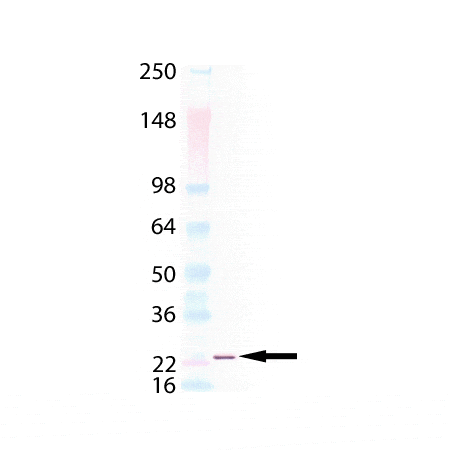
Western Blot Analysis: Lane 1: MW marker, Lane 2: 50 ng of TRAIL (soluble) (human), (recombinant) (His-tag) probed with Anti-6X His tag® antibody.
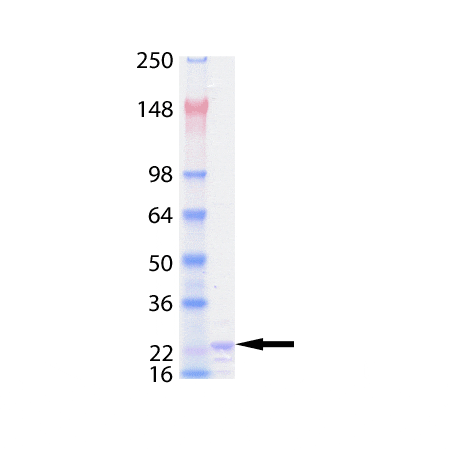
SDS-PAGE analysis: Lane 1: MW marker, Lane 2: 1µg TRAIL (soluble) (human), (recombinant) (His-tag) (Prod. No. BML-SE721).
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
XIAP promotes melanoma growth by inducing tumour neutrophil infiltration: M. Daoud, et al.; EMBO Rep.
23, e53608 (2022),
Abstract;
Plasma-stimulated medium kills TRAIL-resistant human malignant cells by promoting caspase-independent cell death via membrane potential and calcium dynamics modulation: T. Tokunaga, et al.; Int. J. Oncol.
52, 697 (2018),
Abstract;
Full Text
Membrane-proximal TRAIL species are incapable of inducing short circuit apoptosis signaling: Implications for drug development and basic cytokine biology: K. Tatzel, et al.; Sci. Rep.
6, 22661 (2016),
Application(s): Western blot,
Abstract;
Activation of surrogate death receptor signaling triggers peroxynitrite-dependent execution of cisplatin-resistant cancer cells: S. Seah, et al.; Cell Death Dis.
6, e1926 (2015),
Abstract;
Full Text
GDP-mannose-4,6-dehydratase (GMDS) Deficiency Renders Colon Cancer Cells Resistant to Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand (TRAIL) Receptor- and CD95-mediated Apoptosis by Inhibiting Complex II Formation: K. Moriwaki, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
286, 43123 (2011),
Application(s): Death induction and sub-G1 assays of GDP-mannose-4,6-dehydratase-rescued HCT116 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Bortezomib Overcomes Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells in Part through the Inhibition of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Pathway: K.F. Chen, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
284, 11121 (2009),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized Huh-7, Sk-hep1, Hep3B and HCC cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Mechanisms of pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure in immunogenic cell death: T. Panaretakis, et al.; EMBO J.
28, 578 (2009),
Abstract;
Treating Metastatic Solid Tumors With Bortezomib and a Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand Receptor Agonist Antibody: A. Shanker, et al.; J. Natl. Cancer Inst.
100, 649 (2008),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized ACHN, A498, MDA-MB-231 and BT-549 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
A novel natural compound, a cycloanthranilylproline derivative (Fuligocandin B), sensitizes leukemia cells to apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) through 15-deoxy-Δ12, 14 prostaglandin J2 production: H. Hasegawa, et al.; Blood
110, 1664 (2007),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized KOB, KK1, ST1, SO4, HL60, HS-sultan, Ramos, K562, MOLT-4, ATLL and primary ATLL cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Association of the Astrovirus Structural Protein VP90 with Membranes Plays a Role in Virus Morphogenesis: E. Méndez, et al.; J. Virol.
81, 10649 (2007),
Application(s): Death induction of astrovirus-infected Caco-2 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
The Farnesyltransferase Inhibitor Lonafarnib Induces CCAAT/Enhancer-binding Protein Homologous Protein-dependent Expression of Death Receptor 5, Leading to Induction of Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cells: S.Y. Sun, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
282, 18800 (2007),
Application(s): Death induction of H1792, H460 and H157 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Dihydroflavonol BB-1, an extract of natural plant Blumea balsamifera, abrogates TRAIL resistance in leukemia cells: H. Hasegawa, et al.; Blood
107, 679 (2006),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized PBMCs, KOB, ST1, Jurkat, U937, K562, HL60 andRamos cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Nonsecreted Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 (IGFBP-3) Can Induce Apoptosis in Human Prostate Cancer Cells by IGF-independent Mechanisms without Being Concentrated in the Nucleus: N. Bhattacharyya, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
281, 24588 (2006),
Application(s): Death induction of PC-3 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Sensitization of TRAIL-resistant cells by inhibition of heat shock protein 90 with low-dose geldanamycin: Y. Ma, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther.
5, 170 (2006),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized LNCaP and DU145 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
The role of NF-κB-1 and NF-κB-2-mediated resistance to apoptosis in lymphomas: L. Bernal-Mizrachi, et al.; PNAS
103, 9220 (2006),
Application(s): Death induction of 204-3-1, NK-H and NK-92 cells and analysis of resistance to TRAIL-induced cell death of Daudi, SC, F8 and BLA cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Characterization of 8p21.3 chromosomal deletions in B-cell lymphoma: TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 as candidate dosage-dependent tumor suppressor genes: F. Rubio-Moscardo, et al.; Blood
106, 3214 (2005),
Application(s): Death induction of VAL and TRAIL-R1/-R2 restored SU-DHL6 and Namalwa cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Cytoskeleton-mediated death receptor and ligand concentration in lipid rafts forms apoptosis-promoting clusters in cancer chemotherapy: C. Gajate & F. Mollinedo; J. Biol. Chem.
280, 11641 (2005),
Abstract;
Full Text
Human Retinoblastoma Cells Are Resistant to Apoptosis Induced by Death Receptors: Role of Caspase-8 Gene Silencing: V. Poulaki, et al.; Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.
46, 358 (2005),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized Y79, WERI-Rb1 and SK-N-MC cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein inhibition induces apoptosis and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity in human prostate cancer cells: A. Amantana, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther.
3, 699 (2004),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized DU145 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
A Novel Single Amino Acid Deletion Caspase-8 Mutant in Cancer Cells That Lost Proapoptotic Activity: B. Liu, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
277, 30159 (2002),
Application(s): Death induction of MCF7, MDA468, DiFi, HN5, and H460 cells and analysis of resistance to TRAIL-induced cell death of A431 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
An Inducible Pathway for Degradation of FLIP Protein Sensitizes Tumor Cells to TRAIL-induced Apoptosis: Y. Kim, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
277, 22320 (2002),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized PPC-1, PC3, OVCAR-3, SK-OV-3, HT29, COLO205, LNCaP, HeLa, HEY3, and HT1080 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Mifepristone Pretreatment Overcomes Resistance of Prostate Cancer Cells to Tumor Necrosis Factor {alpha}-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand (TRAIL): M.A. Eid, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther.
1, 831 (2002),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized LNCaP and LNCaP C4-2 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Regulation of leukemic cell adhesion, proliferation, and survival by beta-catenin: E.J. Chung, et al.; Blood
100, 982 (2002),
Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
NF-κB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP: O. Micheau, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol.
21, 5299 (2001),
Abstract;
Full Text
Roles of TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: B. Hilliard, et al.; J. Immunol.
15, 166 (2001),
Application(s): Death induction of Jurkat and K562 cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
The cytokines tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand differentially modulate proliferation and apoptotic pathways in human keratinocytes expressing the h: J.R. Basile, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
276, 22522 (2001),
Abstract;
Full Text
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and phorbol ester induce TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) under critical involvement of NF-kappa B essential modulator (NEMO)/IKKgamma: D. Siegmund, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
276, 43708 (2001),
Abstract;
Full Text
Augmentation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand (TRAIL)-induced Apoptosis by the Synthetic Retinoid 6-[3-(1-Adamantyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]-2-naphthalene Carboxylic Acid (CD437) through Up-Regulation of TRAIL Receptors in Human Lung Cancer Cells: S.Y. Sun, et al.; Cancer Res.
60, 7149 (2000),
Application(s): Death induction of sensitized H460, A549, H1944, H1792, H157, H596, NHBE and SAE cells,
Abstract;
Full Text
Combined effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and ionizing radiation in breast cancer therapy: A.M. Chinnaiyan, et al.; PNAS
97, 1754 (2000),
Abstract;
FADD/MORT1 and caspase-8 are recruited to TRAIL receptors 1 and 2 and are essential for apoptosis mediated by TRAIL receptor 2: M.R. Sprick, et al.; Immunity
12, 599 (2000),
Abstract;
Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule: N. Holler, et al.; Nat. Immunol.
1, 489 (2000),
Abstract;
The death domain kinase RIP is essential for TRAIL (Apo2L)-induced activation of IkappaB kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase: Y. Lin et al.; Mol. Cell Biol.
20, 6638 (2000),
Abstract;
Thyroid carcinoma cells are resistant to FAS-mediated apoptosis but sensitive to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand: N.S. Mitsaides et al.; Cancer Res.
60, 4122 (2000),
Abstract;
Full Text
Conversion of membrane-bound Fas(CD95) ligand to its soluble form is associated with downregulation of its proapoptotic activity and loss of liver toxicity: P. Schneider, et al.; J. Exp. Med.
187, 1205 (1998),
Abstract;
Intracellular regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells: T.S. Griffith, et al.; J. Immunol.
161, 2833 (1998),
Abstract;
An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL: G. Pan, et al.; Science
277, 815 (1997),
Abstract;
Characterization of two receptors for TRAIL: P. Schneider, et al.; FEBS Lett.
416, 329 (1997),
Abstract;
Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors: J.P. Sheridan, et al.; Science
277, 818 (1997),
Abstract;
Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP: M. Irmler, et al.; Nature
388, 190 (1997),
Abstract;
Interleukin 1 beta-converting enzyme related proteases/caspases are involved in TRAIL-induced apoptosis of myeloma and leukemia cells: S.M. Mariani et al.; J. Cell. Biol.
137, 221 (1997),
Abstract;
The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL: G. Pan, et al.; Science
276, 111 (1997),
Abstract;
Viral FLICE-inhibitory proteins (FLIPs) prevent apoptosis induced by death receptors: M. Thome, et al.; Nature
386, 517 (1997),
Abstract;
Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family: R.M. Pitti, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
271, 12687 (1996),
Abstract;
Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis: S.R. Wiley, et al.; Immunity
3, 673 (1995),
Abstract;












