Replaces Prod. #: ALX-215-022
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | KCIP-1, Protein kinase C inhibitor protein 1, 14-3-3E |
| |
| Host: | Rabbit |
| |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide corresponding to aa 239-255 (CG239EEQNKEALQDVEDENQ255) of 14-3-3ε. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P62258 (human) |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat
Bovine, Chicken, Rabbit, Sheep
|
| |
| Specificity: | Specific for the ε isoform. |
| |
| Applications: | ELISA, IHC, WB
|
| |
| Recommended Dilutions/Conditions: | Western Blot (HRP/ECL detection, 1:3,000)
Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.
Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| |
| Blocking Peptide: | For Blocking peptide see Prod. No. BML-SP475.
|
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. Neat serum. Contains no preservatives. |
| |
| Handling: | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
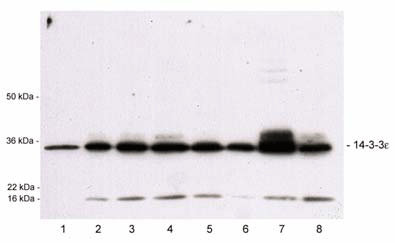
Figure: Western blot analysis of cell lysates using 14-3-3 ε, pAb (Prod. No. BML-SA475). Antibody dilution 1:3’000, blot was developed by HRP/ECL.1. HeLa S100 (cytosol)2. HeLa (whole cell)3. Jurkat 4. MDCK 5. A4316. MDF-77. rat brain 8. PC12
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Unchanged survival rates of 14-3-3gamma knockout mice after inoculation with pathological prion protein: P. Steinacker, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol.
25, 1339 (2005),
Abstract;
Full Text
Interaction of Akt-phosphorylated ataxin-1 with 14-3-3 mediates neurodegeneration in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1: H.K. Chen, et al.; Cell
113, 457 (2003),
Abstract;
Functional specificity in 14-3-3 isoform interactions through dimer formation and phosphorylation. Chromosome location of mammalian isoforms and variants: A. Aitken; Plant Mol. Biol.
50, 993 (2002),
Abstract;
Immunolocalisation of 14-3-3 isoforms in normal and scrapie-infected murine brain: H.C. Baxter, et al.; Neuroscience
109, 5 (2002),
Abstract;
Isoform pattern of 14-3-3 proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: J. Wiltfang, et al.; J. Neurochem.
73, 2485 (1999),
Abstract;
14-3-3 inhibits the Dictyostelium myosin II heavy-chain-specific protein kinase C activity by a direct interaction: identification of the 14-3-3 binding domain: M. Matto-Yelin, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell
8, 1889 (1997),
Abstract;
Full Text
Identification of 14-3-3 proteins in human platelets: effects of synthetic peptides on protein kinase C activation: C.P. Wheeler-Jones, et al.; Biochem. J.
315, 41 (1996),
Abstract;
Full Text
Expression and structural analysis of 14-3-3 proteins: D.H. Jones, et al.; J. Mol. Biol.
245, 375 (1995),
Abstract;
Isoforms of 14-3-3 protein can form homo- and heterodimers in vivo and in vitro: implications for function as adapter proteins: D.H. Jones, et al.; FEBS Lett.
368, 55 (1995),
Abstract;
Purification of 14-3-3 protein and analysis of isoforms in chicken brain: Y. Patel, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta
1222, 405 (1994),
Abstract;
Subcellular localisation of 14-3-3 isoforms in rat brain using specific antibodies: H. Martin, et al.; J. Neurochem.
63, 2259 (1994),
Abstract;
Antibodies against the major brain isoforms of 14-3-3 protein. An antibody specific for the N-acetylated amino-terminus of a protein: H. Martin, et al.; FEBS Lett.
331, 296 (1993),
Abstract;












