Product Details
| Host: | Rabbit |
| |
| Immunogen: | Human erythrocyte-derived proteasomes. |
| |
| Source: | From rabbit serum. |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat
Rabbit, Yeast
|
| |
| Specificity: | Recognizes the 'core' subunits of the 20S proteasome. |
| |
| Applications: | IHC (FS), IP, WB
|
| |
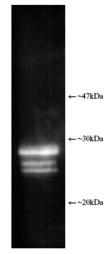
| Application Notes: | Western blot - The antibody has been characterised by single dimension SDS-PAGE using both purified human and yeast 20S proteasome and a number of tissue/cell preparations including a human placental proteasome preparation, a HeLa cell lysate, a RSV 3T3 mouse fibroblast cell lysate, and a yeast whole cell extract. Western blotting shows bands attributable to ‘core’ subunits at ~25-30kDa as shown opposite. Differences in subunit band intensity are noted between the samples. 2-D SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting of purified 20S proteasome shows the presence of five/six spots with the following proteasome subunit correlation: α5/α7, β1, β5, β5i, β7. The 2-D patterns observed with human and mouse derived materials are not identical with some differences being observed in the molecular weights and isoelectric points of some subunits. |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In PBS containing 10mM sodium azide. |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Dilute with PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 and 1% normal goat serum (if a goat anti-rabbit IgG linker antibody is to be used). |
| |
| Handling: | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Aliquot undiluted antibody into smaller volumes (not less than 10µl) prior to freezing if appropriate. The use of high quality ‘antiserum-grade’ plastic or glass vials is recommended. Dilute to working strength with phosphate buffered saline pH 7.2-7.4 and 1% normal goat serum (if a goat anti-rabbit IgG linker antibody is to be used). Store diluted antibody at +2-4°C (do not freeze) and use within 1 month. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Scientific Background: | The proteasome is widely recognised as the central enzyme of non-lysosomal protein degradation. It is responsible for intracellular protein turnover and it is also critically involved in many regulatory processes and, in higher eukaryotes, in antigen processing. The 26S proteasome is the key enzyme of the ubiquitin/ATP-dependent pathway of protein degradation. The catalytic core of this unusually large (2000kDa, 450Å in length) complex is formed by the 20S proteasome, a barrel shaped structure shown by electron microscopy to comprise of four rings each containing seven subunits.
Based on sequence similarity, all fourteen 20S proteasomal subunit sequences may be classified into two groups, α and β, each group having distinct structural and functional roles. The α-subunits comprise the outer rings and the β-subunits the inner rings of the 20S proteasome. Observations of the eukaryotic proteasome and analysis of subunit sequences indicate that each ring contains seven different subunits (α7β7β7α7) with a member of each sub-family represented in each particle. Each subunit is located in a unique position within the α- or β-rings. 120S Proteasomes degrade only unfolded proteins in an energy-independent manner, whereas 26S proteasomes degrade native and ubiquitinylated proteins in an ATP-dependent manner. The native protein substrates are recognised by subunits, some with ATP binding sites, of the outer 19S caps of the 26S proteasome. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
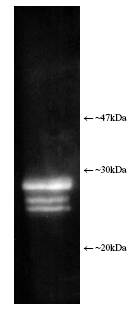
Figure: Luminograph of human erythrocyte-derived 20S proteasome lysate after SDS-PAGE followed by blotting onto PVDF and probing with antibody Prod. No. BML-PW8155. Antibody dilution 1:1000 using ECL procedure (1 min exposure).
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
The molecular network of the proteasome machinery inhibition response is orchestrated by HSP70, revealing vulnerabilities in cancer cells: M. Oroń, et al.; Cell Rep.
40, 111428 (2022),
Abstract;
Immobilized Antibodies on Mercaptophenylboronic Acid Monolayers for Dual-Strategy Detection of 20S Proteasome: M.M. Barsan, et al.; Sensors
21, 2702 (2021),
Abstract;
Full Text
Survivin suppression heightens BZML-induced mitotic catastrophe to overcome multidrug resistance by removing therapy-induced senescent A549/Taxol cells: Z. Bai, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res.
1869, 119174 (2021),
Abstract;
Chemical proteasome inhibition as a novel animal model of inner retinal degeneration in rats: M. Kageyama, et al.; PLoS One
14, e0217945 (2019),
Abstract;
Full Text
Mass spectrometry-based absolute quantification of 20S proteasome status for controlled ex-vivo expansion of Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: T. Menneteau, et al.; Mol. Cell. Proteomics
18, 744 (2019),
Application(s): ELISA based quantification of 20S proteosome in human 293-EBNA cells expressing 20S proteosome,
Abstract;
"Cyt/Nuc," a Customizable and Documenting ImageJ Macro for Evaluation of Protein Distributions Between Cytosol and Nucleus: T. Grune, et al.; Biotechnol J.
13, 1700652 (2018),
Abstract;
TRIM11 activates the proteasome and promotes overall protein degradation by regulating USP14: L. Chen, et al.; Nat. Commun.
9, 1223 (2018),
Abstract;
Full Text
Human Antiviral Protein IFIX Suppresses Viral Gene Expression during Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1) Infection and Is Counteracted by Virus-induced Proteasomal Degradation.: M.S. Crow & I.M. Cristea; Mol. Cell. Proteomics
16, S200 (2017),
Application(s): Immunoaffinity purifications, WB and immunofluorescence ,
Abstract;
Uncovering the SUMOylation and ubiquitylation crosstalk in human cells using sequential peptide immunopurification: F. Lamoliatte, et al.; Nat. Commun.
8, 14109 (2017),
Abstract;
Full Text
The Molecular Chaperone Hsp70 Promotes the Proteolytic Removal of Oxidatively Damaged Proteins by the Proteasome: S. Reeg, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med.
99, 153 (2016),
Application(s): Immunoblot Analysis,
Abstract;
D1 dopamine receptor stimulation impairs striatal proteasome activity in Parkinsonism through 26S proteasome disassembly: P. Barroso-Chinea, et al.; Neurobiol. Dis.
78, 77 (2015),
Application(s): Immunocytochemistry, Western Blotting,
Abstract;
Proteomic identification of hair cell repair proteins in the model sea anemone Nematostella vectensis: P.C. Tang, et al.; Hear. Res.
327, 245 (2015),
Application(s): Inhibition experiments,
Abstract;
Nuclear proteasomes carry a constitutive posttranslational modification which derails SDS-PAGE (but not CTAB-PAGE): D.S. Pitcher, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta
1844, 2222 (2014),
Abstract;
TRIM5α associates with proteasomal subunits in cells while in complex with HIV-1 virions: Z. Lukic, et al.; Retrovirology
8, 93 (2011),
Abstract;
Full Text
General Literature References
Budding yeast Dsk2p is a polyubiquitin-binding protein that can interact with the proteasome: M. Funakoshi et al.; PNAS
99, 745 (2002),
Abstract;
Transient aggregation of ubiquitinated proteins during dendritic cell maturation: H. Lelouard et al.; Nature
417, 177 (2002),
Abstract;
UFD4 lacking the proteasome-binding region catalyses ubiquitination but is impaired in proteolysis: Y. Xie et al.; Nat. Cell. Biol.
4, 1003 (2002),
Abstract;
Subunit arrangement in the human 20S proteasome: F. Kopp et al.; PNAS
94, 2939 (1997),
Abstract;
The 26S proteasome: subunits and functions: K. Tanaka et al.; Molecular Biology Reports
24, 3 (1997),
Abstract;