Replaces Prod. #: ALX-340-029
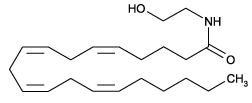
Endogenous [1] ligand for the CB1 receptor (CB1: Ki=52nm; CB2: Ki=1930nm [2]) and TRPV1 (Ki=5.78µM [3,4]). Inhibits NF-κB activation through direct binding to IKKβ [5] and induces apoptosis independently of cannabinoid or vanilloid receptors [6]. Activates the MAP kinase (MAPK/ERK) signalling pathway [7].
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | AEA, N-Arachidonoylethanolamine, (all-Z)-N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenamide |
| |
| Formula: | C22H37NO2 |
| |
| MW: | 347.54 |
| |
| CAS: | 94421-68-8 |
| |
| MI: | 14: 624 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (TLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | Colorless oil. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in ethanol (e.g. at a concentration of 50 mg/ml). It is also soluble in DMSO and dimethyl formamide. |
| |
| Shipping: | Dry Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -80°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored, as supplied, under an inert atmosphere at -80°C. |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light and oxygen. Keep under inert gas. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Anandamide inhibits adhesion and migration of breast cancer cells: C. Grimaldi, et al.; Exp. Cell Res.
312, 363 (2006),
Abstract;
Accumulation of anandamide: Evidence for cellular diversity: C.J. Hillard and A. Jarrahian; Neuropharmacology
48, 1072 (2005),
Abstract;
Anandamide as an intracellular messenger regulating ion channel activity: M. van der Stelt and V. Di Marzo; Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat.
77, 111 (2005),
Abstract;
Anandamide reduces infarct size in rat isolated hearts subjected to ischaemia-reperfusion by a novel cannabinoid mechanism: N.J. Underdown, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol.
146, 809 (2005),
Abstract;
Preferred conformations of endogenous cannabinoid ligand anandamide: J.Z. Chen, et al.; Life Sci.
76, 2053 (2005),
Abstract;
The cardiovascular actions of anandamide: more targets?: M.D. Randall; Br. J. Pharmacol.
145, 565 (2005),
Abstract;
Full Text
Anandamide is an endogenous inhibitor for the migration of tumor cells and T lymphocytes: J. Joseph, et al.; Cancer Immunol. Immunother.
53, 723 (2004),
Abstract;
Anandamide-induced cell death in primary neuronal cultures: role of calpain and caspase pathways: V.A. Movsesyan, et al.; Cell Death Differ.
11, 1121 (2004),
Abstract;
Arachidonylethanolamide induces apoptosis of human glioma cells through vanilloid receptor-1: E. Contassot, et al.; J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol.
63, 956 (2004),
Abstract;
Anandamide induces cell death independently of cannabinoid receptors or vanilloid receptor 1: possible involvement of lipid rafts: K.P. Sarker, et al.; Cell Mol. Life Sci.
60, 1200 (2003),
Abstract;
Anandamide inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activation through a cannabinoid receptor-independent pathway: R. Sancho, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol.
63, 429 (2003),
Abstract;
Anandamide: some like it hot: V. Di Marzo, et al.; TIPS
22, 346 (2001), (Review),
Abstract;
Structure-activity relationship for the endogenous cannabinoid, anandamide, and certain of its analogues at vanilloid receptors in transfected cells and vas deferens: R.A. Ross, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol.
132, 631 (2001),
Abstract;
New perspectives on enigmatic vanilloid receptors: A. Szallasi & V. Di Marzo; TINS
23, 491 (2000), (Review),
Abstract;
Anandamide: a candidate neurotransmitter heads for the big leagues: D.W. Self; Nat. Neurosci.
2, 303 (1999), (Review),
Abstract;
Metabolism of anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol: an historical overview and some recent developments: V. Di Marzo, et al.; Lipids
34, S319 (1999), (Review),
Abstract;
Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide: P.M. Zygmunt, et al.; Nature
400, 452 (1999),
Abstract;
Cannabinoid receptors and their endogenous agonist, anandamide: J. Axelrod & C.C. Felder; Neurochem. Res.
23, 575 (1998), (Review),
Abstract;
Endocannabinoids: a new class of vasoactive substances: M.D. Randall & D.A. Kendall; TIPS
19, 55 (1998), (Review),
Abstract;
Endocannabinoids: endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligands with neuromodulatory action: V. Di Marzo, et al.; TINS
21, 521 (1998), (Review),
Abstract;
Novel analogues of arachidonylethanolamide (anandamide): affinities for the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors and metabolic stability: S. Lin, et al.; J. Med. Chem.
41, 5353 (1998),
Abstract;
The endogenous cannabinoid anandamide inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation: L. De Petrocellis, et al.; PNAS
95, 8375 (1998),
Abstract;
Biochemistry and pharmacology of arachidonylethanolamide, a putative endogenous cannabinoid: C.J. Hillard & W.B. Campbell; J. Lipid Res.
38, 2383 (1997), (Review),
Abstract;
The MAP kinase signal transduction pathway is activated by the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide: M. Wartmann, et al.; FEBS Lett.
359, 133 (1995),
Abstract;
New dawn of cannabinoid pharmacology: W.A. Devane; Trends Pharmacol. Sci.
15, 40 (1994),
Abstract;
Anandamide, an endogenous ligand of the cannabinoid receptor, induces hypomotility and hypothermia in vivo in rodents: J.N. Crawley, et al.; Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav.
46, 967 (1993),
Abstract;
Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids: S. Munro, et al.; Nature
365, 61 (1993),
Abstract;
Pharmacological activity of the cannabinoid receptor agonist, anandamide, a brain constituent: E. Fride & R. Mechoulam; Eur. J. Pharmacol.
231, 313 (1993),
Abstract;
Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor: W.A. Devane, et al.; Science
258, 1946 (1992),
Abstract;