Replaces Prod. #: ALX-350-382
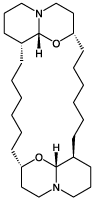
Xestonspongin C is a structurally novel marine alkaloid isolated from the Okinawan sponge Xestospongia sp. It is a potent, cell-permeable inhibitor of IP3 receptor-mediated Ca2+ release (IC50 = 358 nM). However, since xestospongin C also inhibits voltage-dependent Ca2+ and K+ currents at concentrations similar to those which inhibit the IP3 receptor, it can only be regarded as a selective blocker of the IP3 receptor in permeabilized cells and not in cells with intact plasma membranes. Has vasodilatory properties.
Product Details
| Formula: | C28H50N2O2 |
| |
| MW: | 446.7 |
| |
| Source: | Synthetic. |
| |
| CAS: | 88903-69-9 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥90% (TLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to off-white powder. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DMSO or 100% ethanol at 2mM. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light. Packaged under inert gas. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Luminal H2O2 promotes ER Ca2+ dysregulation and toxicity of palmitate in insulin-secreting INS-1E cells: S. Sharifi, et al.; FASEB J.
37, e22685 (2023),
Abstract;
Inhibitory mechanism of xestospongin-C on contraction and ion channels in the intestinal smooth muscle: H. Ozaki, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol.
137, 1207 (2002),
Abstract;
Xestospongin C empties the ER calcium store but does not inhibit InsP3-induced Ca2+ release in cultured dorsal root ganglia neurones: N. Solovyova, et al.; Cell Calcium
21, 49 (2002),
Abstract;
Xestospongin C is a potent inhibitor of SERCA at a vertebrate synapse: A. Castonguay & R. Robitaille; Cell Calcium
32, 39 (2002),
Abstract;
Ca2+ entry mediated by store depletion, S-nitrosylation, and TRP3 channels. Comparison of coupling and function: D.B. van Rossum, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
275, 28562 (2000),
Abstract;
In vivo signal transduction of nociceptive response by kyotorphin (tyrosine-arginine) through Galpha(i)- and inositol trisphosphate-mediated Ca(2+) influx: H. Ueda & M. Inoue; Mol. Pharmacol.
57, 108 (2000),
Abstract;
Xestospongin C, a selective and membrane-permeable inhibitor of IP(3) receptor, attenuates the positive inotropic effect of alpha-adrenergic stimulation in guinea-pig papillary muscle: S. Miyamoto, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol.
130, 650 (2000),
Abstract;
Xestospongin C is an equally potent inhibitor of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor and the endoplasmic-reticulum Ca(2+) pumps: P. De Smet, et al.; Cell Calcium
26, 9 (1999),
Abstract;
New developments in the molecular pharmacology of the myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor: A. Wilcox, et al.; Trends Pharmacol. Sci.
19, 467 (1998),
Abstract;
Xestospongins: potent membrane permeable blockers of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor: J. Gafni, et al.; Neuron
19, 723 (1997),
Abstract;
Clinical and hematological studies on twelve cases of secondary aplastic anemia: M. Kobayashi, et al.; Nippon Ketsueki Gakkai Zasshi
47, 195 (1984),
Abstract;
Structures of xestospongin A,B,C and D, novel vasodilativecompounds from marine sponge, Xestospongia exigua: M. Nakagawa, et al.; Tetrahedron Lett. 25, 3227 (1984),