Replaces Prod. #: ALX-380-002
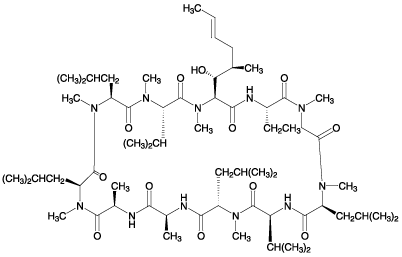
Cyclosporin A (CsA) is an immunosuppressant that has revolutionized organ transplantation through its use in the prevention of graft rejection. CsA binds to cyclophilin and suppresses its proline rotamase activity. The CsA-cyclophilin complex inhibits calcineurin, a type 2B phosphatase. It is an important diagnostic tool for the characterization of permeability transition-related phenomena. It inhibits mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening however, pore inhibition becomes less efficient at increasing Ca2+ loads and inhibition is transient. Inhibits staurosporin-induced apoptosis in cultured neural cells and rotenone-induced apoptosis in PC-12 cells. Inhibits cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Inhibits nitric oxide (NO) synthesis.
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | CsA |
| |
| Formula: | C62H111N11O12 |
| |
| MW: | 1202.6 |
| |
| Source: | Isolated from Fusarium solani |
| |
| CAS: | 59865-13-3 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (Assay) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to off-white powder. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml), methanol, 100% ethanol (25mg/ml), acetone or petroleum ether; insoluble in water. |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Store, as supplied, at -20°C for up to 1 year. Store solutions at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 in CD4+ T cells ameliorates intestinal inflammation: H. Lee, et al.; Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.
15, 439 (2023),
Abstract;
Zebrafish Larvae Position Tracker (Z-LaP Tracker): a high-throughput deep-learning behavioral approach for the identification of calcineurin pathway-modulating drugs using zebrafish larvae: S.V. Gore, et al.; Sci. Rep.
13, 3174 (2023),
Abstract;
Lysophosphatidic Acid Promotes the Expansion of Cancer Stem Cells via TRPC3 Channels in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: N. Hirata, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci.
23, 1967 (2022),
Abstract;
Novel use of FDA-approved drugs identified by cluster analysis of behavioral profiles: S.T. Edmister, et al.; Sci. Rep.
12, 6120 (2022),
Abstract;
Oxidative bursts of single mitochondria mediate retrograde signaling toward the ER: D.M. Booth, et al.; Mol. Cell
81, 3866 (2021),
Abstract;
Full Text
Mitochondrial BK Channel Openers CGS7181 and CGS7184 Exhibit Cytotoxic Properties: B. Augustynek, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci.
19, E353 (2018),
Abstract;
Phosphorylation and inhibition of ceramide kinase by protein kinase C-β: Their changes by serine residue mutations: H. Takahashi, et al.; Cell Signal.
54, 59 (2018),
Abstract;
Differential induction of ATF3 and HO-1 in myeloid cells and keratinocytes via Dimethylfumarate or Cyclosporine A: S. Müller, et al.; J. Dermatol. Sci.
87, 246 (2017),
Application(s): Treatment of human keratinocytes and PBMCs,
Abstract;
Interactions of human P-glycoprotein transport substrates and inhibitors at the drug binding domain: Functional and molecular docking analyses: O. Kadioglu, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol.
104, 42 (2016),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
Monocyte Trafficking, Engraftment, and Delivery of Nanoparticles and an Exogenous Gene into the Acutely Inflamed Brain Tissue - Evaluations on Monocyte-Based Delivery System for the Central Nervous System: H.I. Tong, et al.; PLoS One
11, e0154022 (2016),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
A small molecule with anticancer and antimetastatic activities induces rapid mitochondrial associated necrosis in breast cancer: A. Bastian, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.
353, 392 (2015),
Application(s): Assay,
Abstract;
Full Text
Effects of embryonic cyclosporine exposures on brain development and behavior: D.E. Clift, et al.; Behav. Brain Res.
282, 117 (2015),
Application(s): Cell Culture,
Abstract;
Melatonin suppresses cyclosporine A-induced autophagy in rat pituitary GH3 cells: Y.M. Yoo & E.B. Jeung; J. Pineal Res.
48, 204 (2010),
Abstract;
Rationale for T cell inhibition by cyclosporin A in major autoimmune diseases: G.F. Ferraccioli, et al.; Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.
1051, 658 (2005),
Abstract;
New aspects of cyclosporin a mode of action: from gene silencing to gene up-regulation: L. Mascarell & P. Truffa-Bachi; Mini. Rev. Med. Chem.
3, 205 (2003),
Abstract;
Cyclosporin A binding to mitochondrial cyclophilin inhibits the permeability transition pore and protects hearts from ischaemia/reperfusion injury: A.P. Halestrap, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biochem.
174, 167 (1997),
Abstract;
Cyclosporin A, FK506 and rapamycin: more than just immunosuppression: J. Kunz & M.N. Hall; Trends. Biochem. Sci.
18, 334 (1993),
Abstract;
FK506 and ciclosporin: molecular probes for studying intracellular signal transduction: J. Liu; Trends. Pharmacol. Sci.
14, 182 (1993),
Abstract;
Immunological actions of cyclosporin A in rheumatoid arthritis: D. Yocum; Br. J. Rheumatol.
32 Suppl 1, 38 (1993),
Abstract;
Immunosuppression for organ grafting -- observations on cyclosporin A: R.Y. Calne; Immunol. Rev.
46, 113 (1979),
Abstract;
Cyclosporin A and C-New metabolites from Trichodermapolysporum : M. Dreyfuss, et al.; Europ. J. Appl. Microbiol. 3, 125 (1976),