Replaces Prod. #: ALX-804-151/1
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | B cell maturation protein, TNFRSF 17, CD269 |
| |
| Clone: | Vicky-1 |
| |
| Host: | Rat |
| |
| Isotype: | IgG1 |
| |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant human BCMA extracellular domain (aa 2-54) (Prod. No. ALX-522-026). |
| |
| UniProt ID: | Q02223 |
| |
| Source: | Purified from ascites. |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human
|
| |
| Crossreactivity: | Does not cross-react with mouse BCMA. |
| |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow Cytometry, ICC, WB, FUNC
|
| |
| Recommended Dilutions/Conditions: | Western Blot (1:1,000, colorimetric)
Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.
Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| |
| Application Notes: | Functional Application: blocks binding of BAFF to human BCMA. |
| |
| Purity Detail: | Protein G-affinity purified. |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide. |
| |
| Handling: | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Short Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Scientific Background: | BCMA (B cell maturation) is a nonglycosylated integral membrane type I protein that is preferentially expressed in mature B lymphocytes and belongs structurally to the TNF receptor family. BCMA associates with BAFF, APRIL, TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 1, TRAF2, and TRAF3 and activates NF-κB, Elk-1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. BCMA plays an important role in B cell development, function and regulation. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
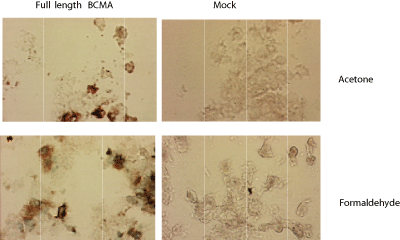
Figure: Immunostaining of HEK 293 cells transfected with a human BCMA expression plasmid (left panel), or mock transfected (right panel). Method: 3 days after transfection of cells with the indicated constructs, cells were fixed with acetone or 4% formaldehyde for 5 min. at room temperature. Slides were blocked with normal IgG, and incubated for 1 hour with 5µg/ml MAb to BCMA (human) (Vicky-1) (Prod. No. ALX-804-151) in 1% BSA in 1x PBS. After washes in PBS, samples were incubated with the secondary antibody for 1 hour, washed in PBS and revealed with StreptABComplex/HRP (Vector) and AEC.
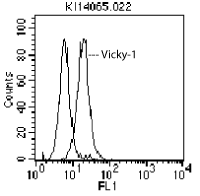
Figure: Detection of endogenous human BCMA with MAb to BCMA (human) (Vicky-1) (Prod. No. ALX-804-151).Method: U266 cells (2x105) were incubated on ice for 30 min. with 0.2µg of MAb to BCMA (human) (Vicky-1) or an isotype control in 25µl FACS buffer (PBS, 5% fetal calf serum, 0.02% azide). The primary antibody was revealed with PAb to Rat IgG (R-PE) and then analyzed by flow cytometry.
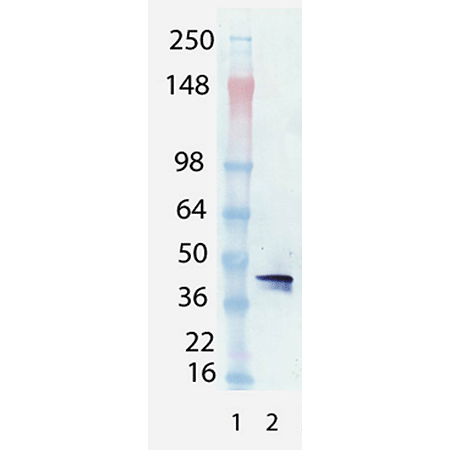
Western blot analysis of BCMA (human) mAb (Vicky-1) (Prod. No. ALX-804-151): Lane 1: MW marker, Lane 2: BCMA (h):Fc (h) (recombinant) (Prod. No. ALX-522-026).
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
APRIL binding to BCMA activates a JNK2-FOXO3-GADD45 pathway and induces a G2/M cell growth arrest in liver cells: G. Notas, et al.; J. Immunol.
189, 4748 (2012),
Abstract;
Detection of the TNFSF members BAFF, APRIL, TWEAK and their receptors in normal kidney and renal cell carcinomas: V. Pelekanou, et al.; Anal. Cell. Pathol. (Amst.)
34, 49 (2011),
Abstract;
Autoantibody-producing RP105(-) B cells, from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, showed more preferential expression of BCMA compared with BAFF-R than normal subjects: S. Koarada, et al.; Rheumatology (Oxford)
49, 662 (2010),
Abstract;
Full Text
Cell to Cell Interaction Can Activate Membrane-bound APRIL Which Are Expressed on Inflammatory Macrophages: L. Sang-Min, et at.; Immune Netw.
10, 173 (2010),
Application(s): Flow Cytometry,
Abstract;
Full Text
The rGel/BLyS fusion toxin inhibits diffuse large B-cell lymphoma growth in vitro and in vivo: M.A. Lyu, et al.; Neoplasia
12, 366 (2010),
Abstract;
Adipocytes as immune cells: differential expression of TWEAK, BAFF, and APRIL and their receptors (Fn14, BAFF-R, TACI, and BCMA) at different stages of normal and pathological adipose tissue development: V.I. Alexaki, et al.; J. Immunol.
183, 5948 (2009),
Abstract;
Expression of TNF-superfamily members BAFF and APRIL in breast cancer: Immunohistochemical study in 52 invasive ductal breast carcinomas: V. Pelekanou, et al.; BMC Cancer
8, 76 (2008),
Abstract;
Full Text
TACI regulates IgA production by APRIL in collaboration with HSPG: D. Sakurai, et al.; Blood
109, 2961 (2007),
Abstract;
General Literature References
BAFF AND APRIL: a tutorial on B cell survival: F. Mackay, et al.; Annu. Rev. Immunol.
21, 231 (2003),
Abstract;
BAFF binds to the tumor necrosis factor receptor-like molecule B cell maturation antigen and is important for maintaining the peripheral B cell population: J.S. Thompson, et al.; J. Exp. Med.
192, 129 (2000),
Abstract;
Full Text
Related Products