Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Lipopolysaccharide from Salmonella abortus equi S-form |
| |
| Source: | Smooth (S)-form LPS, isolated and purified from Salmonella abortus equi by modification of the phenol water extraction and PCP method, converted to the uniform salt form and dissolved in pyrogen-free double distilled water. |
| |
| Concentration: | 1mg/ml |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. Sterile, ready-to-use solution in pyrogen-free double distilled water. |
| |
| Purity: | Absence of detectable protein or DNA contaminants with agonistic TLR activity. |
| |
| Activity: | Strong activator of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4. Does not activate TLR2 or other TLRs as determined with splenocytes and macrophages from TLR4 deficient mice. No further re-extraction required.Smooth (S)-form LPS are commonly the preferred choice for whole animal studies, whereas Rough (R)-form LPS are primarily used in cellular in vitro activation studies. |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | +4°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| |
| Handling: | Do not ingest. Wear gloves and mask when handling this product! Avoid contact through all modes of exposure. LPS compounds are highly pyrogenic. Avoid accidental injection; extreme care should be taken when handling in conjunction with hypodermic syringes Use must be restricted to qualified personnel. Keep sterile. |
| |
| Technical Info/Product Notes: | For the biotinylated LPS, please see Prod. No. ALX-581-150. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
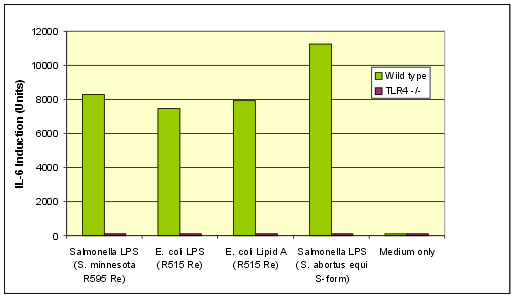
Figure: Activation of macrophages from TLR4 wild type compared to TLR4 deficient mice by LPS and Lipid A from Enzo. Lipid A or LPS concentrations, which induced maximal activation of TLR4 wild type mouse macrophages, were also applied to TLR4 deficient mouse macrophages. 10 units of IL-6 correspond to the detection limit of the IL-6 ELISA.
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Immunostimulatory activity of fluoxetine in macrophages via regulation of the PI3K and P38 signaling pathways: H.T. Önal, et al.; Immunol. Res.
71, 413 (2023),
Abstract;
Voltage-Gated Proton Channel Hv1 Regulates Neuroinflammation and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease Models: M.L. Neal, et al.; Antioxidants
12, 582 (2023),
Abstract;
High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) inhibition attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive dysfunction and sickness-like behavior in mic: D. Ghosh, et al.; Immunol. Res.
70, 633 (2022),
Abstract;
Non-canonical anti-cancer, anti-metastatic, anti-angiogenic and immunomodulatory PDT potentials of water soluble phthalocyanine derivatives with imidazole groups and their intracellular mechanism of action: F. Ayaz, et al.; Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther.
39, 103035 (2022),
Abstract;
Physiological levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 induce a suppressive CD4+ T cell phenotype not reflected in the epigenetic landscape: C. Matos, et al.; Scand. J. Immunol.
95, e13146 (2022),
Abstract;
Postmitotic differentiation of human monocytes requires cohesin-structured chromatin: J. Minderjahn, et al.; Nat. Commun.
13, 4301 (2022),
Abstract;
Specific features of human monocytes activation by monophosphoryl lipid A: R. Chentouh, et al.; Sci. Rep.
8, 7096 (2018),
Abstract;
Full Text
Alternative microglial activation is associated with cessation of progressive dopamine neuron loss in mice systemically administered lipopolysaccharide: E.E. Beier, et al.; Neurobiol. Dis.
108, 115 (2017),
Application(s): Mouse Injection,
Abstract;
Lactic acid delays the inflammatory response of human monocytes: K. Peter, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.
457, 412 (2015),
Application(s): Cell Culture,
Abstract;
Mechanisms of Hypoxic Up-Regulation of Versican Gene Expression in Macrophages: F. Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, et al.; PLoS One
10, e0125799 (2015),
Application(s): Cell Culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
TLR3-mediated CD8+ dendritic cell activation is coupled with establishment of a cell-intrinsic antiviral state: L. Szèles, et al.; J. Immunol.
195, 1025 (2015),
Abstract;
Differential inflammatory response to inhaled lipopolysaccharide targeted either to the airways or the alveoli in man: W. Möller, et al.; PLoS One
7, e33505 (2012),
Abstract;
Full Text
Chemokine Expression by Small Sputum Macrophages in COPD: M. Frankenberger, et al.; Mol. Med.
17, 762 (2011),
Abstract;
Full Text
Evolution of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) recognition and signaling: fish TLR4 does not recognize LPS and negatively regulates NF-kappaB activation: M.P. Sepulcre, et al.; J. Immunol.
182, (2009),
Abstract;
Full Text
Lipopolysaccharide elicits expression of immune-related genes in the silkworm, Bombyx mori: H. Tanaka, et al.; Insect Mol. Biol.
18, 71 (2009),
Abstract;
Increased TNF expression in CD43++ murine blood monocytes: B. Burke, et al.; Immunol. Lett.
118, 142 (2008),
Abstract;
Production of IL-12, IL-23 and IL-27p28 by bone marrow-derived conventional dendritic cells rather than macrophages after LPS/TLR4-dependent induction by Salmonella Enteritidis: S. Siegemund, et al.; Immunobiology
212, 739 (2008),
Abstract;
R-form LPS, the master key to the activation ofTLR4/MD-2-positive cells: M. Huber, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol.
36, 701 (2006),
Abstract;
CD14 is required for MyD88-independent LPS signaling: Z. Jiang, et al.; Nat. Immunol.
6, 565 (2005),
Abstract;
IL-12 family members: differential kinetics of their TLR4-mediated induction by Salmonella Enteritidis and the impact of IL-10 in bone marrow-derived macrophages: N. Schuetze, et al.; Int. Immunol.
17, 649 (2005),
Abstract;
A striking correlation between lethal activity and apoptotic DNA fragmentation of liver in response of D-galactosamine-sensitized mice to a non-lethal amount of lipopolysaccharide: B.R. Zhou, et al.; Acta Pharmacol. Sin.
24, 193 (2003),
Abstract;
Full Text
Toll-like receptor 4 expression levels determine the degree of LPS-susceptibility in mice: C. Kalis, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol.
33, 798 (2003),
Abstract;
Oligosaccharides of Hyaluronan activate dendritic cells via toll-like receptor 4: C. Termeer, et al.; J. Exp. Med.
195, 99 (2002),
Abstract;
Full Text
Isolation and purification of R-form lipopolysaccharides: C. Galanos & O. Lüderitz; Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry
9, 11 (1993),
Abstract;
Preparation and properties of a standardized lipopolysaccharide from salmonella abortus equi (Novo-Pyrexal) : C. Galanos, et al.; Zentralbl. Bakteriol. [Orig. A]
243, 226 (1979),
Abstract;
Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms: C. Galanos & O. Lüderitz; Eur. J. Biochem.
54, 603 (1975),
Abstract;
A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides: C. Galanos, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem.
9, 245 (1969),
Abstract;
Related Products












