Replaces Prod. #: ALX-581-204
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Lipopolysaccharide from E. coli, Serotype R515 (Re) |
| |
| Source: | Rough (R)-form LPS isolated and purified from E. coli R515 (Re mutant) by a modification of the PCP extraction method, converted to the uniform sodium salt form and dissolved in sterile pyrogen-free double distilled water. |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. Sterile, ready-to-use solution in pyrogen-free double distilled water. |
| |
| Purity: | Absence of detectable protein or DNA contaminants with agonistic TLR activity. |
| |
| Activity: | Strong activator of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4. Does not activate TLR2 or other TLRs as determined with splenocytes and macrophages from TLR4 deficient mice. No further re-extraction required.Smooth (S)-form LPS are commonly the preferred choice for whole animal studies, whereas Rough (R)-form LPS are primarily used in cellular in vitro activation studies. |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | +4°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| |
| Handling: | Do not ingest. Wear gloves and mask when handling this product! Avoid contact through all modes of exposure. LPS compounds are highly pyrogenic. Avoid accidental injection; extreme care should be taken when handling in conjunction with hypodermic syringes Use must be restricted to qualified personnel. Keep sterile. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
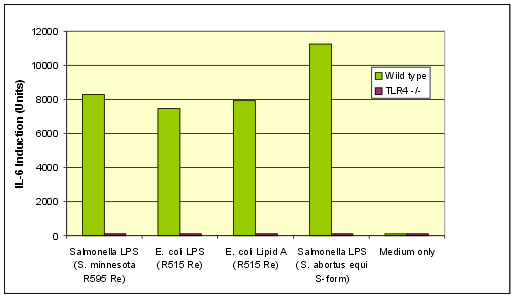
Figure: Activation of macrophages from TLR4 wild type compared to TLR4 deficient mice by LPS and Lipid A from Enzo. Lipid A or LPS concentrations, which induced maximal activation of TLR4 wild type mouse macrophages, were also applied to TLR4 deficient mouse macrophages. 10 units of IL-6 correspond to the detection limit of the IL-6 ELISA.
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Myeloid expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl1 is required in anti-myeloperoxidase vasculitis but myeloperoxidase inhibition is not protective: F.F. Barros, et al.; Kidney Int.
103, 134 (2023),
Abstract;
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase δ Deficiency Protects From Antimyeloperoxidase Vasculitis: F.F. Barrós, et al.; Arthritis Rheumatol.
75, 64 (2023),
Abstract;
Helminth antigens modulate human PBMCs, attenuating disease progression in a humanised mouse model of graft versus host disease: M. Healy, et al.; Exp. Parasitol.
235, 108231 (2022),
Abstract;
LRRK2 is required for CD38-mediated NAADP-Ca2+ signaling and the downstream activation of TFEB (transcription factor EB) in immune cells: N.R. Nabar, et al.; Autophagy
18, 204 (2022),
Abstract;
MK2 Inhibitors as a Potential Crohn’s Disease Treatment Approach for Regulating MMP Expression, Cleavage of Checkpoint Molecules and T Cell Activity: E.J. Lebish, et al.; Pharmaceuticals
15, 1508 (2022),
Abstract;
Protection against severe infant lower respiratory tract infections by immune training: Mechanistic studies: N.M. Troy, et al.; J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.
150, 93 (2022),
Abstract;
The development of novel glucocorticoid receptor antagonists: From rational chemical design to therapeutic efficacy in metabolic disease models: J. Kroon, et al.; Pharmacol. Res.
168, 105588 (2021),
Abstract;
TLR2- and TLR3-activated microglia induce different levels of neuronal network dysfunction in a context-dependent manner: S. Schilling, et al.; Brain Behav. Immun.
17, 889 (2021),
Abstract;
CD244 represents a new therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: L. Agresta, et al.; J. Immunother. Cancer
8, e000245 (2020),
Abstract;
Full Text
Platelets modulate multiple markers of neutrophil function in response to in vitro Toll-like receptor stimulation: K. Hally, et al.; PLoS One
14, e0223444 (2019),
Abstract;
Full Text
Heme oxygenase 2 binds myristate to regulate retrovirus assembly and TLR4 signaling: Y. Zhu, et al.; Cell Host Microbe
21, 220 (2017),
Abstract;
Full Text
Surface LAMP-2 is an endocytic receptor that diverts antigen internalized by human dendritic cells into highly immunogenic exosomes: D.A. Leone, et al.; J. Immunol.
199, 531 (2017),
Application(s): Use with human monocyte-derived dendritic cells,
Abstract;
The shape and size of hydroxyapatite particles dictate inflammatory responses following implantation: F. Lebre, et al.; Sci. Rep.
7, 2922 (2017),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
Use of Toll-like receptor agonists to induce ectopic lymphoid structures in Myasthenia gravis mouse models: M. Robinet, et al.; Front. Immunol.
8, 1029 (2017),
Application(s): In vivo mouse model,
Abstract;
Full Text
Evaluation of NADPH oxidases as drug targets in a mouse model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: T. Seredenina, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med.
97, 95 (2016),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
Fasciola hepatica Surface Coat Glycoproteins Contain Mannosylated and Phosphorylated N-glycans and Exhibit Immune Modulatory Properties Independent of the Mannose Receptor: A. Ravida, et al.; PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis.
10, e0004601 (2016),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
The Sur1-Trpm4 channel regulates NOS2 transcription in TLR4-activated microglia: D.B. Kurland, et al. ; J. Neuroinflammation
13, 130 (2016),
Application(s): LPS activation of TLR4,
Abstract;
Full Text
TLR activation by Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens (GMMA) from lipid A mutants of Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium and Enteritidis: O. Rossi, et al.; Clin. Vaccine Immunol.
23, 304 (2016),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
Neutrophil Recruitment to Lymph Nodes Limits Local Humoral Response to Staphylococcus aureus: O. Kamenyeva, et al.; PLoS Pathog.
11, e1004827 (2015),
Application(s): Cell Culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
Protocatechuic acid inhibits human dendritic cell functional activation: role of PPARγ up-modulation: M. Del Corno, et al.; Immunobiology
219, 416 (2014),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
The Step Further to Understand the Role of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Alpha and Group X Secretory Phospholipase A2 in Allergic Inflammation: Pilot Study: E. Pniewska, et al.; BioMed Res. Int.
2014, 670814 (2014),
Abstract;
Similarities and differences of innate immune responses elicited by smooth and rough LPS: I. Zanoni, et al.; Immunol. Lett.
142, 41 (2012),
Abstract;
Stimulation of TLR4 by recombinant HSP70 requires structural integrity of the HSP70 protein itself: M. Luong, et al.; J. Inflamm. (Lond.)
9, 11 (2012),
Abstract;
Full Text
CD14 and TRIF govern distinct responsiveness and responses in mouse microglial TLR4 challenges by structural variants of LPS: T. Regen, et al.; Brain Behav. Immun.
25, 957 (2011),
Abstract;
Pathways regulating lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophil survival revealed by lentiviral transduction of primary human neutrophils: E.P. Dick, et al.; Immunol.
127, 249 (2009),
Abstract;
Full Text
Human Langerhans cells selectively activated via Toll-like receptor 2 agonists acquire migratory and CD4+T cell stimulatory capacity: M. Peiser, et al.; J. Leukoc. Biol.
83, 1118 (2008),
Abstract;
The role of TLR2 in the inflammatory activation of mouse fibroblasts by human antiphospholipid antibodies: N. Satta, et al.; Blood
109, 1507 (2007),
Abstract;
Full Text
Cooperative molecular and cellular networks regulate Toll-like receptor-dependent inflammatory responses: G.E. Morris, et al.; FASEB J.
20, 2153 (2006),
Abstract;
Full Text
Functional and biochemical characterization of epithelial bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein: G. Canny, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol.
290, G557 (2006),
Abstract;
Full Text
R-form LPS, the master key to the activation ofTLR4/MD-2-positive cells: M. Huber, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol.
36, 701 (2006),
Abstract;
Toll-like receptors TLR2 and TLR4 initiate the innate immune response of the renal tubular epithelium to bacterial products: P. Chowdhury, et al.; Clin. Exp. Immunol.
145, 346 (2006),
Abstract;
Full Text
Trypsin-sensitive modulation of intestinal epithelial MD-2 as mechanism of lipopolysaccharide tolerance: E. Cario, et al.; J. Immunol.
176, 4258 (2006),
Abstract;
Full Text
Inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis by TLR agonists in whole blood: involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and NF-kappaB signaling pathways, leading to increased levels of Mcl-1, A1, and phosphorylated Bad: S. François, et al.; J. Immunol.
174, 3633 (2005),
Abstract;
Full Text
Toll-like receptor 4 signaling regulates cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation and lipid generation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages: H.Y. Qi & J.H. Shelhamer; J. Biol. Chem.
280, 38969 (2005),
Abstract;
Full Text
Isolation and purification of R-form lipopolysaccharides: C. Galanos & O. Lüderitz; Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry
9, 11 (1993),
Abstract;
Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms: C. Galanos & O. Lüderitz; Eur. J. Biochem.
54, 603 (1975),
Abstract;
Full Text
A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides: C. Galanos, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem.
9, 245 (1969),
Abstract;
Related Products












