CNS stimulant. Blocks adenosine A1 and A2A receptors. cAMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Interferes with the uptake and storage of Ca2+ by the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle. Prevents apoptosis and cell cycle effects induced by various chemicals. Inhibits cellular DNA repair mechanisms. Anti-inflammatory.
Product Details
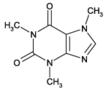
| Alternative Name: | 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthine, 3,7-Dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| |
| Formula: | C8H10N4O2 |
| |
| MW: | 194.2 |
| |
| Source: | Found in tea leaves, coffee beans, cocoa beans, maté leaves, guarana paste and kola nuts. |
| |
| CAS: | 58-08-2 |
| |
| MI: | 14: 1636 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
| |
| Identity: | Determined by IR. |
| |
| Appearance: | White to colorless powder. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in chloroform, 100% alcohol or hot water. |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | Ambient |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
A comprehensive study of the differences in protein expression and chemical constituents in tea leaves (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis) with different maturity using a combined proteomics and metabolomics method: Z. Sun, et al.; Food Res. Int.
157, 111397 (2022),
Abstract;
New insights into the influences of baking and storage on the nonvolatile compounds in oolong tea: A nontargeted and targeted metabolomics study: J. Peng, et al.; Food Chem.
375, 131872 (2022),
Abstract;
Impact of Various Microbial-Fermented Methods on the Chemical Profile of Dark Tea Using a Single Raw Tea Material: J. Shi, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem.
69, 4210 (2021),
Abstract;
Time effect of rutaecarpine on caffeine pharmacokinetics in rats: R.K. Estari, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Rep.
28, 101121 (2021),
Abstract;
Study of the dynamic changes in the Non-volatile chemical constituents of black tea during fermentation processing by a Non-targeted metabolomics approach: J. Tan, et al.; Food Res. Int. 79, 106 (2016),
The enigmatic effects of caffeine in cell cycle and cancer: A. M. & Bode and Z. Dong; Cancer Lett.
247, 26 (2007), (Review),
Abstract;
Immunomodulatory effects of caffeine: friend or foe: L. A. Horrigan, et al.; Pharmacol. Ther.
111, 877 (2006), (Review),
Abstract;
Novel neuroprotection by caffeine and adenosine A(2A) receptor antagonists in animal models of Parkinson’s disease: A. Kalda, et al.; J. Neurol. Sci.
248, 9 (2006), (Review),
Abstract;
Acute effects of caffeine on arterial stiffness, wave reflections, and central aortic pressures: T.G. Papaioannou, et al.; Am. J. Hypertens.
18, 129 (2005), (Review),
Abstract;
Caffeine and the dopaminergic system: O. Cauli & M. Morelli; Behav. Pharmacol.
16, 63 (2005), (Review),
Abstract;
Caffeine as an analgesic adjuvant: a review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action: J. Sawynok & T.L. Yaksh; Pharmacol. Rev.
45, 43 (1993),
Abstract;
Caffeine prevents apoptosis and cell cycle effects induced by camptothecin or topotecan in HL-60 cells: F. Traganos, et al.; Cancer Res.
53, 4613 (1993),
Abstract;
Multiple effects of caffeine on calcium current in rat ventricular myocytes: I. Zahradnik & P. Palade; Pfluegers Arch.
424, 129 (1993),
Abstract;
Analogues of caffeine and theophylline: effect of structural alterations on affinity at adenosine receptors: J.W. Daly, et al.; J. Med. Chem.
29, 1305 (1986),
Abstract;