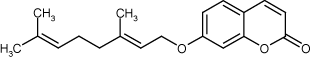
Anti-inflammatory and chemopreventive compound. Exerts tumor preventive effects through apoptosis. Suppresses cell proliferation and lipid peroxidation. Acts as an agonist of PPARs. Induces phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes.
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | 7-Geranyloxycoumarin, 7-[(2E)-3,7-Dimethylocta-2,6-dienoxy]chromen-2-one |
| |
| Formula: | C19H22O3 |
| |
| MW: | 298.4 |
| |
| Source: | Isolated from citrus fruit. |
| |
| CAS: | 495-02-3 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥95% (UHPLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to beige solid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in methanol or 100% ethanol. |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Citrus auraptene acts as an agonist for PPARs and enhances adiponectin production and MCP-1 reduction in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: K. Kuroyanagi, et al.; BBRC
366, 219 (2008),
Abstract;
Citrus auraptene targets translation of MMP-7 (matrilysin) via ERK1/2-dependent and mTOR-independent mechanism: K. Kawabata, et al.; FEBS Lett.
580, 5288 (2006),
Abstract;
Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of natural and semisynthetic geranyloxycoumarins: M. Curini, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.
14, 2241 (2004),
Abstract;
Cell proliferation in cancer prevention; effects of preventive agents on estrogen-related endometrial carcinogenesis model and on an in vitro model in human colorectal cells: H. Mori, et al.; Mutat. Res.
480-481, 201 (2001),
Abstract;
Immunomodulatory action of citrus auraptene on macrophage functions and cytokine production of lymphocytes in female BALB/c mice: T. Tanaka, et al.; Carcinogenesis
20, 1471 (1999),
Abstract;
Full Text
Citrus auraptene exerts dose-dependent chemopreventive activity in rat large bowel tumorigenesis: the inhibition correlates with suppression of cell proliferation and lipid peroxidation and with induction of phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes: T. Tanaka, et al.; Cancer Res.
58, 2550 (1998),
Abstract;
Full Text