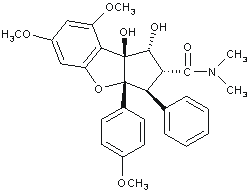
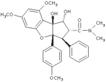
Immunosuppressant. Potent inhibitor of NF-κB activation in T cells, with an almost complete inhibition at 200nM. Suppresses cytokine production (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2 and IL-4) and inhibits NF-AT in peripheral blood T cells at concentrations that do not impair NF-κB and AP-1 activities. In contrast to the immunosuppressant cyclosporin A (Prod. No. BML-A195), rocaglamide does not inhibit calcineurin phosphatase activity. Induces apoptosis.
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Rocaglamide A |
| |
| Formula: | C29H31NO7 |
| |
| MW: | 505.6 |
| |
| Source: | Synthetic |
| |
| CAS: | 84573-16-0 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to off-white sticky solid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DMSO, 100% ethanol or methanol. |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
The prohibitin-binding compound fluorizoline inhibits mitophagy in cancer cells: S. Núñez-Vázquez, et al.; Oncogenesis
10, 64 (2021),
Abstract;
New acyclic bis phenylpropanoid and neolignans, from Myristica fragrans Houtt., exhibiting PARP-1 and NF-κB inhibitory effects: U.M. Acuna, et al.; Food. Chem.
202, 269 (2016),
Application(s): Positive control,
Abstract;
Rocaglamide and a XIAP inhibitor cooperatively sensitize TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in Hodgkin's lymphomas: M. Giaisi, et al.; Int. J. Cancer.
131, 1003 (2012),
Abstract;
Rocaglamide sensitizes leukemic T cells to activation-induced cell death by differential regulation of CD95L and c-FLIP expression.: J.Y. Zhu, et al.; Cell Death Differ.
16, 1289 (2009),
Abstract;
The traditional Chinese herbal compound rocaglamide preferentially induces apoptosis in leukemia cells by modulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase activities: J.Y. Zhu, et al.; Int. J. Cancer
121, 1839 (2007),
Abstract;
Potent cytotoxic rocaglamide derivatives from the fruits of Amoora cucullata: P. Chumkaew, et al.; Chem. Pharm. Bull.
54, 1344 (2006),
Abstract;
Potential of cyclopenta[b]benzofurans from Aglaia species in cancer chemotherapy: S. Kim, et al.; Anticancer Agents Med. Chem.
6, 319 (2006),
Abstract;
Rocaglamide derivatives are immunosuppressive phytochemicals that target NF-AT activity in T cells: P. Proksch, et al.; J. Immunol.
174, 7075 (2005),
Abstract;
Full Text
Rocaglamide derivatives are potent inhibitors of NF-kappa B activation in T-cells: B. Baumann, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
277, 44791 (2002),
Abstract;
Full Text
New insecticidal rocaglamide derivatives and related compounds from Aglaia oligophylla: M. Dreyer, et al.; J. Nat. Prod.
64, 415 (2001),
Abstract;
Rocaglamides, glycosides, and putrescine bisamides from Aglaia dasyclada: Chaidir, et al.; J. Nat. Prod.
64, 1216 (2001),
Abstract;
Cyclopenta[b]benzofurans from Aglaia species with pronounced antifungal activity against rice blast fungus (Pyricularia grisea): D. Engelmeier, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem.
48, 1400 (2000),
Abstract;
Insecticidal rocaglamide derivatives from Aglaia spectabilis (Meliaceae): C. Schneider, et al.; Phytochemistry
54, 731 (2000),
Abstract;
X-ray crystal structure of rocaglamide, a novel antileukemic 1H-cyclopenta-(b)-benzofuran from Aglaia elliptofolia: M.L. King, et al.; J. C. S. Chem. Commun. 20, 1150 (1982),
Related Products