Replaces Prod. #: BML-GR301
Potent antitumor agent. Inhibitor of DNA-topoisomerase I. Activates p53 resulting in upregulated expression of TRAIL-R2 (DR5) and Bak to overcome TRAIL resistance in Bax-deficient human colon carcinoma cells. Inhinbits Tat-mediated transactivation of HIV-1. Induces apoptosis in osteosarcoma and hepatoma cells. Suppresses nitric oxide (NO) biosynthesis.
Product Details
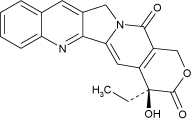
| Formula: | C20H16N2O4 |
| |
| MW: | 348.4 |
| |
| Source: | Isolated from Camptotheca acuminata seeds. |
| |
| CAS: | 7689-03-4 |
| |
| MI: | 14: 1735 |
| |
| RTECS: | UQ0492000 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| |
| Identity: | Determined by IR. |
| |
| Appearance: | Light yellow powder or needle-shaped crystal. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml), methanol (40mg/ml), 0.1N sodium hydroxide (50mg/ml) or acetic acid; insoluble in water. |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | +4°C |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light and moisture. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
An Atypical, Staged Cell Death Pathway Induced by Depletion of SNARE-Proteins MUNC18-1 or Syntaxin-1: F.M. Feringa, et al.; J. Neurosci.
43, 347 (2023),
Abstract;
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in mouse decidua during early pregnancy: X.W. Gu, et al.; Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.
434, 48 (2016),
Application(s): Cell culture, stromal cells,
Abstract;
The p53 binding protein PDCD5 is not rate-limiting in DNA damage induced cell death: F. J. Bock, et al.; Sci. Rep.
5, 11268 (2015),
Application(s): Cell Culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
Three-Dimensional (3D) Cell Cultures in Cell-based Assays for in-vitro Evaluation of Anticancer Drugs: A.F. Adcock, et al.; J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech.
6, 3 (2015),
Application(s): Drug Treatment,
Full Text
Sod1 Loss Induces Intrinsic Superoxide Accumulation Leading to p53-Mediated Growth Arrest and Apoptosis: K. Watanabe, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci.
14, 10998 (2013),
Application(s): Treatment of NIH3T3 cell to induce DNA damage,
Abstract;
Full Text
The antiviral adaptor proteins Cardif and Trif are processed and inactivated by caspases: M. Rebsamen, et al.; Cell Death Differ.
15, 1804 (2008),
Abstract;
The effects of camptothecin on RNA polymerase II transcription: roles of DNA topoisomerase I:: G. Capranico, et al.; Biochimie
89, 482 (2007),
Abstract;
Camptothecin and its analogues: a review on their chemotherapeutic potential: D. Sriram, et al.; Nat. Prod. Res.
19, 393 (2005), Review,
Abstract;
Camptothecin and taxol: historic achievements in natural products research: N.H. Oberlies & D.J. Kroll; J. Nat. Prod.
67, 129 (2004), Review,
Abstract;
Reversal of multidrug resistance-associated protein-mediated daunorubicin resistance by camptothecin: D. Chauvier, et al.; J. Pharm. Sci.
91, 1765 (2002),
Abstract;
Camptothecin suppresses nitric oxide biosynthesis in RAW 264.7 macrophages: W.F. Chiou, et al.; Life Sci.
69, 625 (2001),
Abstract;
Camptothecin and taxol: discovery to clinic: M.E. Wall; Med. Res. Rev.
18, 299 (1998), Review,
Abstract;
Camptothecin-induced apoptosis in p53-null human leukemia HL60 cells and their isolated nuclei: effects of the protease inhibitors Z-VAD-fmk and dichloroisocoumarin suggest an involvement of both caspases and serine proteases: T. Shimizu & Y. Pommier; Leukemia
11, 1238 (1997),
Abstract;
Chemotherapeutic agent CPT-11 induces the new expression of the apoptosis initiator to the cytoplasm: A. Suzuki & M. Kato; Exp. Cell. Res.
227, 154 (1996),
Abstract;
The anti-cancer drug camptothecin inhibits elongation but stimulates initiation of RNA polymerase II transcription: M. Ljungman & P.C. Hanawalt; Carcinogenesis
17, 31 (1996),
Abstract;
The cell cycle effects of camptothecin: Z. Darzynkiewicz, et al.; Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.
803, 93 (1996),
Abstract;
Differential stabilization of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I cleavable complexes by camptothecin derivatives: A. Tanizawa, et al.; Biochemistry
34, 7200 (1995),
Abstract;
Forskolin and camptothecin induce a 30 kDa protein associated with melatonin production in Y79 human retinoblastoma cells: J.L. Janavs, et al.; J. Neurosci.
15, 298 (1995),
Abstract;
Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis: D.W. Nicholson, et al.; Nature
376, 37 (1995),
Abstract;
Camptothecin inhibits Tat-mediated transactivation of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus: C.J. Li, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
269, 7051 (1994),
Abstract;
Camptothecins: from bench research to hospital wards: M. Potmesil; Cancer Res.
54, 1431 (1994), (Review),
Abstract;
RNA synthesis inhibitors increase melatonin production in Y79 human retinoblastoma cells: J.L. Janavs, et al.; Mol. Brain Res.
23, 47 (1994),
Abstract;
The current status of camptothecin analogues as antitumor agents: W.J. Slichenmyer, et al.; J. Natl. Cancer Inst.
85, 271 (1993), (Review),
Abstract;
Irreversible trapping of the DNA-topoisomerase I covalent complex. Affinity labeling of the camptothecin binding site: R.P. Hertzberg, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
265, 19287 (1990),
Abstract;
On the mechanism of topoisomerase I inhibition by camptothecin: evidence for binding to an enzyme-DNA complex: R.P. Hertzberg, et al.; Biochemistry
28, 4629 (1989),
Abstract;
Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I: Y.H. Hsiang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
260, 14873 (1985),
Abstract;
Plant Antitumor Agents. I. The Isolation and Structure of Camptothecin, a Novel Alkaloidal Leukemia and Tumor Inhibitor from Camptotheca acuminata: M.E. Wall, et al.; JACS
88, 3888 (1966),
Abstract;
Related Products