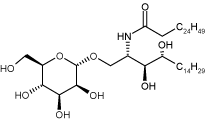
Potent stimulator of natural killer T (NKT) cells expressing the invariant Vα19-Jα26 T cell receptor α chain (Vα19 NKT cells).
Product Details
| Alternative Name: | α-ManCer |
| |
| Formula: | C50H99NO9 |
| |
| MW: | 858.3 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥95% (TLC and NMR) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to brown powder. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in pyridine or warm DMSO (4mg/ml). |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Short Term Storage: | +4°C |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Handling: | After reconstitution, aliquot into glass vials. |
| |
| Scientific Background: | Natural killer T cells (NKT cells) are important regulators of the immune system. They share properties of both innate as well as adaptive immunity. They express T cell receptors (TCR) on their surface consisting of an invariable α-chain and a somewhat variable β-chain. The majority of NKT cells express the invariable α-chain Vα14-Jα18 (Vα14) in mouse or its homolog in humans Vα24-Jα18 (Vα24). Vα14 NKT cells recognize α-GalCer presented by CD1d. NKT cells expressing the invariant Vα19-Jα26 TCR α-chain (Vα19 NKT cells) have been found in peripheral blood lymphocytes and in the liver. They recognize α-ManCer presented by MR1 (Major histocompatibility complex, class I-related) and respond with production of large amounts of immunoregulatory cytokines. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Modulation of Valpha19 NKT cell immune responses by alpha-mannosyl ceramide derivatives consisting of a series of modified sphingosines: M. Shimamura, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol.
37, 1836 (2007),
Abstract;
Induction of promotive rather than suppressive immune responses from a novel NKT cell repertoire Valpha19 NKT cell with alpha-mannosyl ceramide analogues consisting of the immunosuppressant ISP-I as the sphingosine unit: M. Shimamura, et al.; Eur. J. Med. Chem.
41, 569 (2006),
Abstract;
Synthetic alpha-mannosyl ceramide as a potent stimulant for an NKT cell repertoire bearing the invariant Valpha19-Jalpha26 TCR alpha chain: N. Okamoto, et al.; Chem. Biol.
12, 677 (2005),
Abstract;
General Literature References
CD1d-lipid-antigen recognition by the semi-invariant NKT T-cell receptor: N.A. Borg, et al.; Nature
448, 44 (2007),
Abstract;
Germline-encoded recognition of diverse glycolipids by natural killer T cells: J.P. Scott-Browne, et al.; Nat. Immunol.
8, 1105 (2007),
Abstract;
Modulation of Valpha19 NKT cell immune responses by alpha-mannosyl ceramide derivatives consisting of a series of modified sphingosines: M. Shimamura, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol.
37, 1836 (2007),
Abstract;
Synthetic alpha-mannosyl ceramide as a potent stimulant for an NKT cell repertoire bearing the invariant Valpha19-Jalpha26 TCR alpha chain: N. Okamoto, et al.; Chem. Biol.
12, 677 (2005),
Abstract;
Presence of a novel subset of NKT cells bearing an invariant V(alpha)19.1-J(alpha)26 TCR alpha chain: M. Shimamura & Y.Y. Huang; FEBS Lett.
516, 97 (2002),
Abstract;
CD1d-restricted mouse V alpha 14 and human V alpha 24 T cells: lymphocytes of innate immunity: K. Benlagha & A. Bendelac; Semin. Immunol.
12, 537 (2000),
Abstract;
CD1d-restricted and TCR-mediated activation of valpha14 NKT cells by glycosylceramides: T. Kawano, et al.; Science
278, 1626 (1997),
Abstract;
Mouse CD1-specific NK1 T cells: development, specificity, and function: A. Bendelac, et al.; Annu. Rev. Immunol.
15, 535 (1997),
Abstract;