Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Heat shock protein 70, HSP70 |
| |
| MW: | ~70kDa |
| |
| Source: | Produced in E. coli. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P0A6Y8 (strain K12) |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In 40mM TRIS, pH 7.5, containing 80mM sodium chloride, 0.8mM DTT, 0.08mM PMSF, and 20% glycerol. |
| |
| Purity: | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE; Western blot) |
| |
| Purity Detail: | Purified by multi-step chromatography. |
| |
| Applications: | ELISA, WB
Activity assay, in vitro Assay
|
| |
| Application Notes: | ATPase activity assay (positive). Western blot control. |
| |
| Shipping: | Dry Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -80°C |
| |
| Scientific Background: | DnaK possesses an autophosphorylation activity and a weak 5-nucleotidase activity, cleaving the 5 phosphate groups from both ribose and deoxyribose nucleotides. The role of DnaK in ATP-dependent protein-protein interactions has been extended to normal E. coli physiology, where, like eukaryotic Hsp70 homologs, it is thought to participate in the assembly/disassembly of protein complexes. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
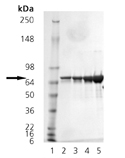
SDS-PAGE analysis of DnaK: Lane 1: MWM, Lanes 2-5: 0.5, 1, 2, 5µg of Prod. No. ADI-SPP-630.
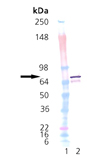
Western Blot Analysis of DnaK: Lane 1: MWM, Lanes 2: 100ng of Prod. No. ADI-SPP-630; probed with Prod. No. ADI-SPA-880.
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
GmDNJ1, a type-I heat shock protein 40 (HSP40), is responsible for both Growth and heat tolerance in soybean: K.P. Li, et al.; Plant Direct
5, e00298 (2021),
Abstract;
Full Text
Protein polarization driven by nucleoid exclusion of DnaK(HSP70)-substrate complexes: C. Collet, et al.; Nat. Commun.
9, 2027 (2018),
Abstract;
Full Text
Bacterial Hsp70 (DnaK) and mammalian Hsp70 interact differently with lipid membranes: V. Lopez, et al.; Cell Stress Chaperones
21, 609 (2016),
Abstract;
Full Text
Scope and limitations of the designer proline-rich antibacterial peptide dimer, A3-APO, alone or in synergy with conventional antibiotics: J.r. Otvos, et al. ; Peptides
29, 1878 (2008),
Application(s): WB ,
Abstract;
Monitoring of the heat-shock response in Escherichia coli using an optical biosensor: C.F. Mandenius, et al. ; Anal. Biochem.
322, 156 (2003),
Application(s): EIA ,
Abstract;
Conserved amino acid residues within the amino-terminal domain of ClpB are essential for the chaperone activity: M. Zolkiewski, et al. ; J. Mol. Biol.
321, 111 (2002),
Abstract;
NEMO trimerizes through its coiled-coil C-terminal domain: M. Veron, et al. ; J. Biol. Chem.
277, 17464 (2002),
Application(s): In Vitro Assay ,
Abstract;
Possible association of non-binding of HSP70 to HLA-DRB1 peptide sequences and protection from rheumatoid arthritis: G.E. Dannecker, et al. ; Immunogenetics
54, 67 (2002),
Abstract;
The conserved helix C region in the superfamily of interferon-gamma /interleukin-10-related cytokines corresponds to a high-affinity binding site for the HSP70 chaperone DnaK: B. Walker, et al. ; J. Biol. Chem.
277, 25668 (2002),
Abstract;
Related Products












