-
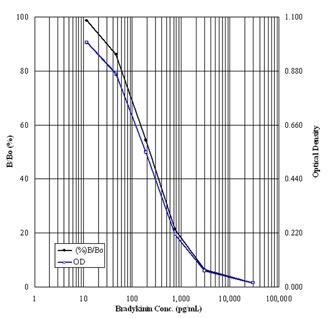
Sensitive, reliably measure as little as 24.8 pg/ml of Bradykinin
-
Rapid results in just 3 hours from up to 41 samples in duplicate
-
Broad dynamic range to easily quantify high and low levels of Bradykinin
-
Easy-to-use liquid color-coded reagents reduce errors
The Bradykinin EIA kit is a colorimetric, competitive immunoassay kit with results in 3 hours.
Please mouse over
Product Details
| Sensitivity: | 24.8 pg/ml (range 11.7-30,000 pg/ml) |
| |
| Assay Time: | 3 hours |
| |
| Applications: | ELISA, Colorimetric detection
|
| |
| Application Notes: | For the quantitative determination of species independent Bradykinin in plasma, serum and urine samples. |
| |
| Wavelength: | 450 nm |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Species independent
|
| |
| Crossreactivity: | Bradykinin (100%) Lys-Bradykinin (Kallidin) (100%) and Les-des-Arg9-Bradykinin (<1%), BK1-5 stable degradion product (<0.1%) |
| |
| Quantity: | 1 x 96-well plate |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Store all components at +4ºC, except Standard at -20ºC. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Short Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Contents: | Microtiter Plate, Conjugate, Antibody, Assay Buffer 16, Wash Buffer Concentrate, Standard, TMB Substrate, Stop Solution 2, Streptavidin-HRP |
| |
| Scientific Background: | Bradykinin was discovered in 1949 as a substance generated from a globulin precursor in plasma by the action of proteases. Its name indicates that is causes a slow movement of the gut. As early as 1909 it was noted that substances found in urine, which were later identified as kinins, have hypotensive actions. Kinins are effectors of vasodilation, vascular permeability, NO release and arachidonic acid mobilization. They are important regulators of blood pressure, kidney function and heart function, and they are also involved in inflammation. Bradykinin is generated from the blood globulin kininogen HK, by the action of the kallikrein system in blood (related to the blood clotting cascade) but can also be generated in other tissues and organs. Besides kallikrein, other proteases such as plasmin may also release bradykinin. Several peptidases can degrade kinins, includ-ing Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE), a metalloproteinase which converts Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II and destroys bradykinin. Plasma bradykinin is rapidly degraded to a smaller stable peptide (BK1-5) form. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P01042 (human) |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
| Compatibility: | This product is compatible with the Absorbance 96 Plate Reader.
 |
| |
Product Literature References
Dysregulation of the kallikrein-kinin system in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with severe COVID-19: C.P. Martens, et al.; EBioMedicine
83, 104195 (2022),
Abstract;
Activation of angiotensin type 2 receptor attenuates testosterone-induced hypertension and uterine vascular resistance in pregnant rats: J.S. Mishra & S. Kumar; Biol. Reprod.
2021, ioab051 (2021),
Abstract;
gC1qR Antibody Can Modulate Endothelial Cell Permeability in Angioedema: M. Fandaros, et al.; Inflammation
1007, 10753 (2021),
Abstract;
Plasma contact factors as novel biomarkers for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease: J. Park, et al.; Biomark. Res.
9, 5 (2021),
Abstract;
Full Text
The Expression of RAAS Key Receptors, Agtr2 and Bdkrb1, Is Downregulated at an Early Stage in a Rat Model of Wolfram Syndrome: M. Punapart, et al.; Genes (Basel)
12, 1717 (2021),
Abstract;
An antibody against HK blocks Alzheimer's disease peptide β-amyloid-induced bradykinin release in human plasma: Z.L. Chen, et al.; PNAS
116, 22921 (2019),
Abstract;
Full Text
Serum bradykinin levels as a diagnostic marker in cervical cancer with a potential mechanism to promote VEGF expression via BDKRB2: Y. Zhou, et al.; Int. J. Oncol.
55, 131 (2019),
Application(s): ELISA using human plasma,
Abstract;
Post-translational modifications of eNOS augment nitric oxide availability and facilitates hypoxia adaptation in Ladakhi women: Pooja, et al.; Nitric Oxide
78, 103 (2018),
Application(s): ELISA using human plasma,
Abstract;
Protocols to assess coagulation following in vitro infection with hemorrhagic fever viruses: M.L. Tursiella, et al.; Methods Mol. Biol.
1604, 405 (2018),
Abstract;
Intestinal ischemic preconditioning ameliorates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats: role of heme oxygenase 1 in the second window of protection: S. Kageyama, et al.; Liver Transpl.
21, 112 (2015),
Application(s): Bradykinin levels in rat serum,
Abstract;
Comparative effects of a novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor versus captopril on plasma angiotensins after myocardial infarction: J. Flores-Monroy, et al.; Pharmacology
94, 21 (2014),
Application(s): Bradykinin levels in rat plasma,
Abstract;
High molecular weight kininogen binds phosphatidylserine and opsonizes urokinase plasminogen activator receptor-mediated efferocytosis: A. Yang, et al.; J. Immunol.
192, 4398 (2014),
Application(s): Bradykinin levels in human plasma,
Abstract;
Full Text
Related Products