Replaces Prod. #: ALX-380-027
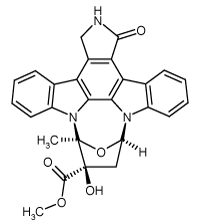
Alkaloid isolated from soil fungi. General, cell permeable protein kinase inhibitor. Acts by binding to the ATP binding domain of the kinase. Potent inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II. Inhibits myosin light chain kinase, cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), protein kinase C (PKC) (Ki=25nM), trk tyrosine kinase family members (gp140trk; IC50 =3nM) and cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG). Binds with high affinity to neuroblastoma membrane (2.7nM), promoting survival of primary neuronal cultures (75nM) and induction of neurite outgrowth in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells along with phosphorylation of pp125 focal adhesion protein tyrosine kinase. Induces apoptosis.
Product Details
| Formula: | C27H21N3O5 |
| |
| MW: | 467.5 |
| |
| CAS: | 99533-80-9 |
| |
| RTECS: | NZ0550000 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | Lyophilized solid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in DMSO (1mg/ml) or dimethyl formamide (1mg/ml). |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored, as supplied, at -20°C. Stock solutions are stable for up to 3 months at -20°C. |
| |
| Handling: | Protect from light. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Mountain-cultivated ginseng protects against cognitive impairments in aged GPx-1 knockout mice via activation of Nrf2/ChAT/ERK signaling pathway: B.T. Nguyen, et al.; J. Ginseng Res.
47, 561 (2023),
Abstract;
Development of actionable targets of multi-kinase inhibitors (AToMI) screening platform to dissect kinase targets of staurosporines in glioblastoma cells: O.V. Denisova, et al.; Sci. Rep.
12, 13796 (2022),
Abstract;
Involvement of Rac1 in macrophage activation by brain-derived neurotrophic factor: S. Sasaki, et al.; Mol. Biol. Rep.
48, 5249 (2021),
Abstract;
Self-amplified BDNF transcription is a regulatory system for synaptic maturation in cultured cortical neurons: S. Nakajima, et al. ; Neurochem. Int.
91, 55 (2015),
Application(s): Cell culture ,
Abstract;
K252a and staurosporine microbial alkaloid toxins as prototype of neurotropic drugs: P. Lazarovici, et al.; Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.
391, 367 (1996), Review,
Abstract;
K-252a induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase and neurite outgrowth in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells: A.C. Maroney, et al.; J. Neurochem.
64, 540 (1995),
Abstract;
K-252a promotes survival and choline acetyltransferase activity in striatal and basal forebrain neuronal cultures: M.A. Glicksman, et al.; J. Neurochem.
64, 1502 (1995),
Abstract;
Membranes of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells contain specific binding sites for [3H]K-252A: E. Knight, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.
211, 511 (1995),
Abstract;
Staurosporine, K-252a, and K-252b stabilize calcium homeostasis and promote survival of CNS neurons in the absence of glucose: B. Cheng, et al.; J. Neurochem.
62, 1319 (1994),
Abstract;
Ecto-protein kinase and surface protein phosphorylation in PC12 cells: interactions with nerve growth factor: Z. Pawlowska, et al.; J. Neurochem.
60, 678 (1993),
Abstract;
K-252a and staurosporine promote choline acetyltransferase activity in rat spinal cord cultures: M.C. Glicksman, et al.; J. Neurochem.
61, 210 (1993),
Abstract;
Staurosporine-related compounds, K252a and UCN-01, inhibit both cPKC and nPKC: K. Mizuno, et al.; FEBS Lett.
330, 114 (1993),
Abstract;
K-252 compounds: modulators of neurotrophin signal transduction: B. Knusel & F. Hefti; J. Neurochem.
59, 1987 (1992),
Abstract;
K-252a and staurosporine selectively block autophosphorylation of neurotrophin receptors and neurotrophin-mediated responses: S.H. Nye, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell
3, 677 (1992),
Abstract;
K-252a inhibits nerve growth factor-induced trk proto-oncogene tyrosine phosphorylation and kinase activity: M.M. Berg, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
267, 13 (1992),
Abstract;
Full Text
K252a is a selective inhibitor of the tyrosine protein kinase activity of the trk family of oncogenes and neurotrophin receptors: P. Tapley, et al.; Oncogene
7, 371 (1992),
Abstract;
pp42/44MAP kinase is a component of the neurogenic pathway utilized by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells: E.D. Lloyd & M.W. Wooten; J. Neurochem.
59, 1099 (1992),
Abstract;
Differentiation of PC12 cells with K-ras: comparison with nerve growth factor: D.L. Simpson, et al.; J. Neurosci. Res.
28, 486 (1991),
Abstract;
Potent and preferential inhibition of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by K252a and its derivative, KT5926: Y. Hashimoto, et al.; BBRC
181, 423 (1991),
Abstract;
K252a is a potent and selective inhibitor of phosphorylase kinase: L.H. Elliott, et al.; BBRC
171, 148 (1990),
Abstract;
Staurosporine, K-252 and UCN-01: potent but nonspecific inhibitors of protein kinases: U.T. Ruegg & G.M. Burgess; TIPS
10, 218 (1989), (Review),
Abstract;
K-252 compounds, novel and potent inhibitors of protein kinase C and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases: H. Kase, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.
142, 436 (1987),
Abstract;
K252a, a new inhibitor of protein kinase C, concomitantly inhibits 40K protein phosphorylation and serotonin secretion in a phorbol ester-stimulated platelets: K. Yamada, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.
144, 35 (1987),
Abstract;
K-252a, a potent inhibitor of protein kinase C from microbial origin: H. Kase, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo)
39, 1059 (1986),
Abstract;
The structures of the novel protein kinase C inhibitors K-252a, b, c and d: T. Yasuzawa, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo)
39, 1072 (1986),
Abstract;