Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 |
| |
| Clone: | 6H2.1 |
| |
| Host: | Mouse |
| |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant human PTEN. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P60484 |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat
|
| |
| Specificity: | Recognizes an epitope between aa 304-403. |
| |
| Applications: | ELISA, ICC, IHC, IP, WB
|
| |
| Recommended Dilutions/Conditions: | Immunoprecipitation (5µg)
Western Blot (1-5µg/ml)
Suggested dilutions/conditions may not be available for all applications.
Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each application. |
| |
| Application Notes: | Detects a band of ~60kDa by Western blot. |
| |
| Purity Detail: | Protein A-affinity purified. Sterile filtered. |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In PBS. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
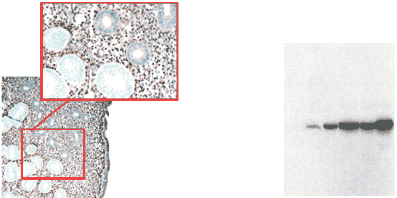
Figure: Left) PTEN non-expressing neoplastic endometrial glands in a background of normal expressing glands and stroma. Right) Single band specificity of MAb to PTEN 6H2.1 on PTEN expressing cancer cell lines.
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Molecular identification of latent precancers in histologically normal endometrium: G.L. Mutter, et al.; Cancer Res.
61, 4311 (2001),
Abstract;
Full Text
Altered PTEN expression as a diagnostic marker for the earliest endometrial precancers: G.L. Mutter, et al.; J. Natl. Cancer Inst.
92, 924 (2000),
Abstract;
Changes in endometrial PTEN expression throughout the human menstrual cycle: G.L. Mutter, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.
85, 2334 (2000),
Abstract;
Full Text
Immunohistochemical evidence of loss of PTEN expression in primary ductal adenocarcinomas of the breast: A. Perren, et al.; Am. J. Pathol.
155, 1253 (1999),
Abstract;
Full Text
PTEN suppresses breast cancer cell growth by phosphatase activity- dependent G1 arrest followed by cell death: L.P. Weng, et al.; Cancer Res.
59, 5808 (1999),
Abstract;
Full Text












