Product Details
| MW: | ~17kDa |
| |
| Source: | Produced in E. coli. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P51668 |
| |
| Formulation: | Liquid. In 20mM TRIS-HCl, pH 8.0, containing 0.5mM DTT. |
| |
| Purity: | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| |
| Application Notes: | Useful for in vitro ubiquitinylation reactions. The His-tagged version of this enzyme is not susceptible to self-ubiquitinylation, which can occur with GST-tagged versions. |
| |
| Shipping: | Dry Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -80°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Enzyme is not stable to multiple freeze/thaw cycles. |
| |
| Handling: | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| |
| Scientific Background: | UbcH5a is highly homologous to the S. cerevisiae Ubc4/5 family of E2 enzymes demonstrated to be essential for degradation of regulatory and abnormal proteins. UbcH5a, together with UbcH5b and UbcH5c, are the most active class of E2 enzymes in cell extracts and are associated with regulation of a number of transcription factors. Specifically, UbcH5a stimulates the conjugation of ubiquitin to the tumor suppressor p53.
A number of E2s in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their homologues have been identified. One such family of E2s is the UBC4/5, characterized as essential for the degradation of short-lived, regulatory and abnormal proteins. Protein levels of S. cerevisiae UbC4/5 are up-regulated in response to stress, and their loss results in severe effects on cellular functions. A human gene product that is 79% identical to S. cerevisiae UBC4/5 in amino-acid sequence was identified as UbcH5a. In addition, two other human members of this highly conserved E2 class were also cloned and designated as UbcH5b and UbcH5c, having 88% and 89% identity to UbcH5a, respectively. Members of the UbcH5a/b/c are the most active class of E2s in cell extracts. The importance of this enzyme class is underscored by the critical role of UBC4/5 in S. cerevisiae. UbcH5a stimulates the conjugation of ubiquitin to the tumour-repressor p53 in the presence of E6-AP and E63. Moreover, UbcH5 family is implicated in c-fos recognition, the modulation of which is controlled by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. UbcH5b and UbcH5c are associated with the signal-induced conjugation and subsequent degradation of IκBα in the presence of the SCF complexes (Skp/Cul/F-Box). UbcH5c also catalyses the ubiquitination leading to the processing of p105 precursor to form p50, a subunit of the heterodimeric transcription factor NF-κB. The range and diversity of substrates and E3s with which this class of E2 enzymes interact, suggest their complex roles in cellular functions require to be studied further. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
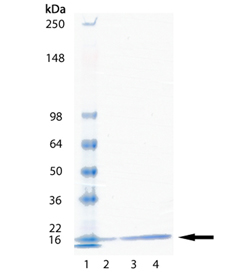
SDS-PAGE Analysis: Lane 1: Molecular weight marker; Lane 2: 1.0 µg; Lane 3: 2 µg; Lane 4: 5 µg of purified Human UbcH5a.
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Protocol to detect in vitro and in cell ubiquitylation of mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma by mitochondrial E3 ligase MITOL: M. Hussein, et al.; STAR Protoc.
3, 101710 (2022),
Abstract;
Phosphoribosylation of Ubiquitin Promotes Serine Ubiquitination and Impairs Conventional Ubiquitination: S. Bhogaraju, et al.; Cell
167, 1636 (2016),
Abstract;