Replaces Prod. #: ALX-306-002
Common component of cell membranes, often as phosphatidyl conjugates. Is a potent (IC50=1-3 µM) and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. Inhibition is competitive with diacylglycerol, phorbol dibutyrate and Ca2+ and it also inhibits PKC activation by other lipids. It acts on an equimolar basis with 1,2-dioleoylglycerol and does not affect other kinases such as MLCK and PKA. It is active in intact cells and has been identified as an endogenous constituent in HL-60 cells, neutrophils, rat liver, and brain and mouse tissues. Other activities include inhibition of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase, Na+,K+-ATPase, CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase, calmodulin-dependent enzymes, binding of factor VII to tissue factor, binding of thyrotropin releasing hormone to its receptor and activation of EGF receptor kinase, phospholipase D and casein kinase II.
Product Details
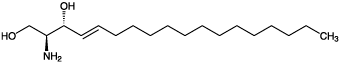
| Alternative Name: | D(+)-erythro-1,3-Dihydroxy-2-amino-4- trans-octadecene |
| |
| Formula: | C18H37NO2 |
| |
| MW: | 299.5 |
| |
| CAS: | 123-78-4 |
| |
| MI: | 14: 8747 |
| |
| Purity: | ≥98% (TLC) |
| |
| Appearance: | White to off-white solid. |
| |
| Solubility: | Soluble in 100% ethanol (25mg/ml warm) or DMSO (25mg/ml warm). |
| |
| Shipping: | Ambient Temperature |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored, as supplied, at -20°C. Stock solutions are stable for up to 3 months at -20°C. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Long-chain bases of sphingolipids are transported into cells via the acyl-CoA synthetases: T. Narita, et al.; Sci. Rep.
6, 25469 (2016),
Application(s): Cell culture,
Abstract;
Full Text
Modulation of protein kinase C and diverse cell functions by sphingosine--a pharmacologically interesting compound linking sphingolipids and signal transduction: A.H. Merrill Jr., et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta
1010, 131 (1989),
Abstract;
Structural requirements for long-chain (sphingoid) base inhibition of protein kinase C in vitro and for the cellular effects of these compounds: A.H. Merrill Jr., et al.; Biochemistry
28, 3138 (1989),
Abstract;
Free sphingoid bases in normal murine tissues: T. Kobayashi, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem.
172, 747 (1988),
Abstract;
Modulation of the free sphingosine levels in human neutrophils by phorbol esters and other factors: E. Wilson, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
263, 9304 (1988),
Abstract;
Quantitation of free sphingosine in liver by high-performance liquid chromatography: A.H. Merrill Jr., et al.; Anal. Biochem.
171, 373 (1988),
Abstract;
Regulation of protein kinase C by lysophospholipids. Potential role in signal transduction: K. Oishi, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
263, 6865 (1988),
Abstract;
Inhibition of phorbol ester-dependent differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemic (HL-60) cells by sphinganine and other long-chain bases: A.H. Merrill Jr., et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
261, 12610 (1986),
Abstract;
Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets: Y.A. Hannun, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
261, 12604 (1986),
Abstract;