Product Details
| Alternative Name: | Tumor necrosis factor-α, TNFSF 2 |
| |
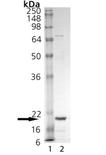
| MW: | ~20kDa (SDS-PAGE). |
| |
| Source: | Produced in E. coli. The extracellular domain of mouse TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α) (aa 77-235) is fused at the N-terminus to a linker peptide (8 aa) and a FLAG®-tag. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P06804 |
| |
| Gene/Protein Identifier: | A002291 (UCSD Signaling Gateway ID) |
| |
| Concentration: | 1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| |
| Purity: | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) |
| |
| Endotoxin Content: | <0.1EU/µg purified protein (LAL test; Associates of Cape Cod). |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat
|
| |
| Specificity: | Binds to human, mouse and rat TNF-R1 and less efficiently to TNF-R2. In the presence of cross-linking enhancer (see Set Prod. No. ALX-850-061), TNF-α shows a significantly higher affinity for TNF-R2 than for TNF-R1, mimicking the characteristics of membrane-bound TNF-α. |
| |
| Applications: | ELISA
|
| |
| Application Notes: | ELISA: binds to human TNF-R1 receptor. |
| |
| Reconstitution: | Reconstitute with 50µl sterile water. Further dilutions should be made with medium containing 5% fetal calf serum. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| |
| Handling: | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| |
| Technical Info/Product Notes: | Historical lots have shown that it exerts its biological activity in a concentration range of 0.5-1ng/ml (WEHI 164 cells).
FLAG is a registered trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
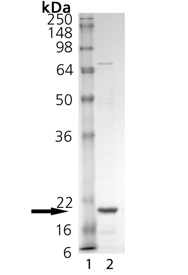
SDS-PAGE Analysis of TNF-α (soluble) (mouse), (recombinant). Lane 1: MW Marker, Lane 2: 1 µg TNF-α
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
RNPS1 inhibits excessive tumor necrosis factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor signaling to support hematopoiesis in mice: X. Zhong, et al.; PNAS
119, e2200128119 (2022),
Abstract;
SMYD2 targets RIPK1 and restricts TNF-induced apoptosis and necroptosis to support colon tumor growth: Y.Q. Yu, et al.; Cell Death Dis.
13, 52 (2022),
Abstract;
Simultaneous Inhibition of Three Major Cytokines and Its Therapeutic Effects: A Peptide-Based Novel Therapy against Endotoxemia in Mice: H.J. Shih, et al.; J. Pers. Med.
11, 436 (2021),
Abstract;
K63-linked ubiquitination regulates RIPK1 kinase activity to prevent cell death during embryogenesis and inflammation: Y. Tang, et al.; Nat. Commun.
10, 4157 (2019),
Abstract;
RIPK1 and Caspase-8 Ensure Chromosome Stability Independently of Their Role in Cell Death and Inflammation: G. Liccardi, et al.; Mol. Cell
73, 413 (2019),
Abstract;
Full Text
Ubiquitination of RIPK1 suppresses programmed cell death by regulating RIPK1 kinase activation during embryogenesis: X. Zhang, et al.; Nat. Commun.
10, 4158 (2019),
Abstract;
Full Text
Ubiquitin-Mediated Regulation of RIPK1 Kinase Activity Independent of IKK and MK2: A. Annibaldi, et al.; Mol. Cell
69, 566 (2018),
Abstract;
Full Text
MK2 Phosphorylates RIPK1 to Prevent TNF-Induced Cell Death: I. Jaco, et al.; Mol. Cell
66, 698 (2017),
Abstract;
Full Text
A novel TNFR1-triggered apoptosis pathway mediated by class IA PI3Ks in neutrophils: B. Geering, et al.; Blood
117, 5953 (2011),
Application(s): Death assay on mouse neutrophils,
Abstract;
Full Text
RasGAP-derived fragment N increases the resistance of beta cells towards apoptosis in NOD mice and delays the progression from mild to overt diabetes: N. Bulat, et al.; PLoS One
6, e22609 (2011),
Abstract;
Full Text
Inhibition of interleukin 1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling through the alternatively spliced, short form of MyD88 is due to its failure to recruit IRAK-4: K. Burns, et al.; J. Exp. Med.
197, 263 (2003),
Abstract;
Full Text
Conversion of membrane-bound Fas(CD95) ligand to its soluble form is associated with downregulation of its proapoptotic activity and loss of liver toxicity: P. Schneider, et al.; J. Exp. Med.
187, 1205 (1998),
Abstract;
Full Text
General Literature References
The transmembrane form of tumor necrosis factor is the prime activating ligand of the 80 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor: M. Grell, et al.; Cell
83, 793 (1995),
Abstract;
The TNF receptor superfamily of cellular and viral proteins: activation, costimulation, and death: C.A. Smith, et al.; Cell
76, 959 (1994),
Abstract;
Tumor necrosis factor: a pleiotropic cytokine and therapeutic target: K.J. Tracey & A. Cerami; Annu. Rev. Med.
45, 491 (1994),
Abstract;