Product Details
| Alternative Name: | CD95, APO-1, TNFRSF 6 |
| |
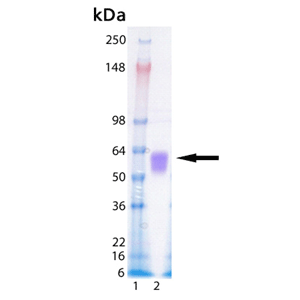
| MW: | ~56 kDa |
| |
| Source: | Produced in HEK 293 cells. The extracellular domain of human Fas (CD95; APO-1) (aa 7-154) is fused to the Fc portion of human IgG1. |
| |
| UniProt ID: | P25445 |
| |
| Concentration: | 1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| |
| Purity: | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| |
| Purity Detail: | Purified by multi-step chromatography. |
| |
| Endotoxin Content: | <0.1EU/µg purified protein (LAL test; Associates of Cape Cod). |
| |
| Species reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat
|
| |
| Specificity: | Binds human, mouse and rat FasL (APO-1L; CD95L; CD178). |
| |
| Applications: | ELISA
|
| |
| Application Notes: | ELISA: binds to FasL at 10-100 ng/ml. |
| |
| Reconstitution: | Reconstitute with 50µl sterile water. Further dilutions can be made with medium containing 5% fetal calf serum or a carrier protein. |
| |
| Shipping: | Blue Ice |
| |
| Long Term Storage: | -20°C |
| |
| Use/Stability: | Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| |
| Handling: | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| |
| Technical Info/Product Notes: | Historical data has shown that Fas inhibits the activity of human and mouse soluble Fas (sFasL) and thereby sFasL-mediated lysis of Fas sensitive cells in a concentration range of 20-100µg/ml. When used with cross-linking enhancer (see Prod. No. ALX-203-001), the inhibitory activity of rhFas:Fc is increased approximately 20- to 50-fold. Concentrations of rhFas:Fc required to inhibit may vary depending on the cell viability and on the concentrations of sFasL used to kill the cells. |
| |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
| |
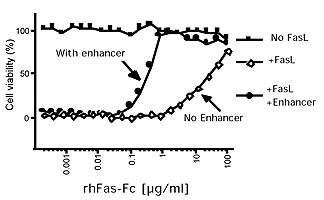
Figure: Inhibition of FasL, Soluble (human) (rec.) (Prod. No.
ALX-522-001)-mediated lysis. Fas (human):Fc (human) (rec.) (Prod. No.
ALX-522-002) exerts its inhibitory activity in a concentration range of 0.5-5µg/ml in the presence of the enhancer (1µg/ml).
Method: Mouse A20 B lymphoma cells (50’000 cells in 100µl DMEM medium containing 5% fetal calf serum) were incubated with 0.2µg/ml FasL, Soluble (human) (rec.) and increasing concentrations of Fas (human):Fc (human) (rec.) in the presence and the absence of 1µg/ml enhancer) in a 96-well plate for 16 hours at 37°C. Concentrations of Fas (human):Fc (human) (rec.) required to inhibit may vary depending on the cell type studied and on the concentration of rhsFasL used to kill cells. Cell viability was determined using an MTT-based cell proliferation assay kit."
Please mouse over
Product Literature References
Combination Therapy with c-Met and Src Inhibitors Induces Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis of Merlin-Deficient Schwann Cells and Suppresses Growth of Schwannoma Cells: M.A. Fuse, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther.
16, 2387 (2017),
Abstract;
Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) promotes tumor cell death by inducing macrophage membrane tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL): T.C. Ho, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
286, 35943 (2011),
Abstract;
Full Text
Proteasome inhibition can induce an autophagy-dependent apical activation of caspase-8: M.A. Laussmann, et al.; Cell Death Differ.
18, 1584 (2011),
Abstract;
Th17 cells enhance viral persistence and inhibit T cell cytotoxicity in a model of chronic virus infection: W. Hou, et al.; J. Exp. Med.
206, 313 (2009),
Abstract;
Full Text
High expression of Fas ligand by synovial fluid-derived gamma delta T cells in Lyme arthritis: K. Roessner, et al.; J. Immunol.
170, 2702 (2003),
Abstract;
Full Text
Two adjacent trimeric Fas ligands are required for Fas signaling and formation of a death-inducing signaling complex: N. Holler, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol.
23, 1428 (2003),
Abstract;
Full Text
Productive HIV-1 infection of primary CD4+ T cells induces mitochondrial membrane permeabilization leading to a caspase-independent cell death: F. Petit et al; J. Biol. Chem.
277, 1477 (2002),
Abstract;
Full Text
Estrogen Receptor–Mediated, Nitric Oxide–Dependent Modulation of the Immunologic Barrier Function of the Endothelium: C. Amant, et al.; Circulation
104, 2576 (2001),
Application(s): Cytotoxicity assay with HUVEC & Jurkat cells,
Abstract;
Mechanisms underlying neuronal death induced by chromogranin A-activated microglia: J. Ciesielski-Treska, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
276, 13113 (2001),
Abstract;
Full Text
T cell costimulation by the TNF ligand BAFF: B. Huard et al.; J. Immunol.
167, 6225 (2001),
Abstract;
Cysteine 230 is essential for the structure and activity of the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL: J.L. Bodmer, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
275, 20632 (2000),
Abstract;
Full Text
Development of improved soluble inhibitors of FasL and CD40L based on oligomerized receptors: N. Holler, et al.; J. Immunol. Methods
237, 159 (2000),
Abstract;
TGF-beta induces the expression of the FLICE-inhibitory protein and inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis of microglia: R. Schlapbach, et al.; Eur. J. Immunol.
30, 3680 (2000),
Abstract;
Characterization of Fas (Apo-1, CD95)-Fas ligand interaction: P. Schneider, et al.; J. Biol. Chem.
272, 18827 (1997),
Abstract;
Full Text
Related Products